Mre11 complex links sister chromatids to promote repair of a collapsed replication fork
- PMID: 30104346
- PMCID: PMC6126713
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1808189115
Mre11 complex links sister chromatids to promote repair of a collapsed replication fork
Abstract
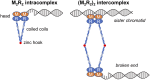
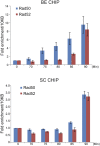
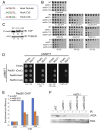
Collapsed replication forks, which are a major source of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), are repaired by sister chromatid recombination (SCR). The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) protein complex, assisted by CtIP/Sae2/Ctp1, initiates SCR by nucleolytically resecting the single-ended DSB (seDSB) at the collapsed fork. The molecular architecture of the MRN intercomplex, in which zinc hooks at the apices of long Rad50 coiled-coils connect two Mre112-Rad502 complexes, suggests that MRN also structurally assists SCR. Here, Rad50 ChIP assays in Schizosaccharomyces pombe show that MRN sequentially localizes with the seDSB and sister chromatid at a collapsed replication fork. Ctp1, which has multivalent DNA-binding and DNA-bridging activities, has the same DNA interaction pattern. Provision of an intrachromosomal repair template alleviates the nonnucleolytic requirement for MRN to repair the broken fork. Mutations of zinc-coordinating cysteines in the Rad50 hook severely impair SCR. These data suggest that the MRN complex facilitates SCR by linking the seDSB and sister chromatid.
Keywords: Mre11; Rad50; double-strand break repair; genome maintenance; recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Release of Ku and MRN from DNA ends by Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 is required for homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002271. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21931565 Free PMC article.
-
Nonhomologous End-Joining with Minimal Sequence Loss Is Promoted by the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1-Ctp1 Complex in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Genetics. 2017 May;206(1):481-496. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.200972. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28292918 Free PMC article.
-
Mre11 ATLD17/18 mutation retains Tel1/ATM activity but blocks DNA double-strand break repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11435-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks954. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23080121 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-regulated binding of Ctp1 to Nbs1 is critical for repair of DNA double-strand breaks.Cell Cycle. 2010 Apr 15;9(8):1516-22. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.8.11260. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20421724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CtIP/Ctp1/Sae2, molecular form fit for function.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Aug;56:109-117. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.06.013. Epub 2017 Jun 9. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28623092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catalysis-dependent and redundant roles of Dma1 and Dma2 in maintenance of genome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100721. Epub 2021 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33933452 Free PMC article.
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Assays to Study Mitotic Recombination Outcomes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 10;11(1):79. doi: 10.3390/genes11010079. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaping the BRCAness mutational landscape by alternative double-strand break repair, replication stress and mitotic aberrancies.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 May 7;49(8):4239-4257. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab151. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33744950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic requirements for repair of lesions caused by single genomic ribonucleotides in S phase.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 3;14(1):1227. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36866-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36869098 Free PMC article.
-
The Ku complex promotes DNA end-bridging and this function is antagonized by Tel1/ATM kinase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 28;51(4):1783-1802. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad062. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36762474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera A, García-Muse T. Causes of genome instability. Annu Rev Genet. 2013;47:1–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

