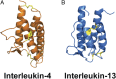
Interleukin 4 is inactivated via selective disulfide-bond reduction by extracellular thioredoxin
- PMID: 30104382
- PMCID: PMC6126747
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1805288115
Interleukin 4 is inactivated via selective disulfide-bond reduction by extracellular thioredoxin
Abstract
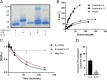
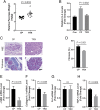
Thioredoxin 1 (TRX), an essential intracellular redox regulator, is also secreted by mammalian cells. Recently, we showed that TRX activates extracellular transglutaminase 2 via reduction of an allosteric disulfide bond. In an effort to identify other extracellular substrates of TRX, macrophages derived from THP-1 cells were treated with NP161, a small-molecule inhibitor of secreted TRX. NP161 enhanced cytokine outputs of alternatively activated macrophages, suggesting that extracellular TRX regulated the activity of interleukin 4 (IL-4) and/or interleukin 13 (IL-13). To test this hypothesis, the C35S mutant of human TRX was shown to form a mixed disulfide bond with recombinant IL-4 but not IL-13. Kinetic analysis revealed a kcat/KM value of 8.1 μM-1⋅min-1 for TRX-mediated recognition of IL-4, which established this cytokine as the most selective partner of extracellular TRX to date. Mass spectrometry identified the C46-C99 bond of IL-4 as the target of TRX, consistent with the essential role of this disulfide bond in IL-4 activity. To demonstrate the physiological relevance of our biochemical findings, recombinant TRX was shown to attenuate IL-4-dependent proliferation of cultured TF-1 erythroleukemia cells and also to inhibit the progression of chronic pancreatitis in an IL-4-driven mouse model of this disease. By establishing that IL-4 is posttranslationally regulated by TRX-promoted reduction of a disulfide bond, our findings highlight a novel regulatory mechanism of the type 2 immune response that is specific to IL-4 over IL-13.
Keywords: M2; disulfide bond; interleukin 4; macrophages; thioredoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Holmgren A, Lu J. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: Current research with special reference to human disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;396:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura H. Thioredoxin as a key molecule in redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004;6:15–17. - PubMed
-
- Rubartelli A, Bajetto A, Allavena G, Wollman E, Sitia R. Secretion of thioredoxin by normal and neoplastic cells through a leaderless secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24161–24164. - PubMed
-
- Lillig CH, Holmgren A. Thioredoxin and related molecules—From biology to health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007;9:25–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

