The N-terminal polypeptide derived from vMIP-II exerts its anti-tumor activity in human breast cancer by regulating lncRNA SPRY4-IT1
- PMID: 30104400
- PMCID: PMC6200706
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20180411
The N-terminal polypeptide derived from vMIP-II exerts its anti-tumor activity in human breast cancer by regulating lncRNA SPRY4-IT1
Abstract
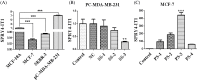
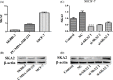
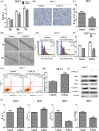
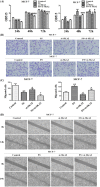
Accumulating evidence demonstrates that long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) sprouty4-intron transcript 1 (lncRNA SPRY4-IT1) plays a vital role in the development of breast cancer. However, the underlying mechanism has not been eventually illuminated. We aimed to explore the biological activity of lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 in breast cancer cells and whether N-terminal polypeptide derived from viral macrophage inflammatory protein II (NT21MP) could exert its anti-tumor effect by regulating lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 and its target gene SKA2 Real-time RT-PCR, Western blotting, wound healing, and invasion assays were used to achieve this goal. We found that lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 was highly expressed in breast cancer cells. Moreover, NT21MP markedly inhibited biological effects of breast cancer cells by regulating lncRNA SPRY4-IT1, which was partially achieved through SKA2. Our findings suggested that lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 could serve as a novel biomarker by NT21MP for breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; NT21MP; SKA2; SPRY4-IT1.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures








References
-
- Donepudi M.S., Kondapalli K., Amos S.J. and Venkanteshan P. (2014) Breast cancer statistics and markers. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 10, 506–511 - PubMed
-
- Lei H. Gao Y. and Xu X. (2017) LncRNA TUG1 influences papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration and EMT formation through targeting miR-145. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 22, 1–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

