Impact of Zinc oxide nanoparticles on eggplant (S. melongena): studies on growth and the accumulation of nanoparticles
- PMID: 30104442
- PMCID: PMC8676606
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0237
Impact of Zinc oxide nanoparticles on eggplant (S. melongena): studies on growth and the accumulation of nanoparticles
Abstract
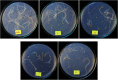
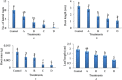
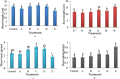
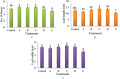
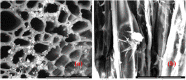
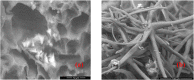
The increasing use of nanoparticles and their occurrence in the environment has made it imperative to elucidate their impact on the environment. Although several studies have advanced the authors' understanding of nanoparticle-plant interactions, their knowledge of the exposure of plants to nanoparticles and their effects on edible crop plants remain meager and is often paradoxical. The aim of this study was to increase their knowledge on the effect of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on eggplant seed germination and seedling growth. ZnO nanoparticles had a negative effect on the growth of eggplant in plant tissue-culture conditions, as the growth of seedlings decreased with the increase in the concentration of ZnO nanoparticles. In contrast, ZnO nanoparticles enhanced eggplant growth under greenhouse conditions. The accumulation of ZnO nanoparticles in various parts of eggplant was observed through scanning electron microscopy of both plant tissue-culture and greenhouse-raised eggplant seedlings. To the best of their knowledge, this is the first study to report on ZnO nanoparticle accumulation in eggplant and its effect on seed germination and seedling growth.
Figures
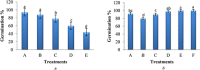
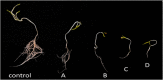





References
-
- Rogers L.: ‘Safety fears over ‘nano’ anti‐aging cosmetics’. The Sunday Times. Available at http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/uk/article544891.ece, 17 July 2005
-
- Lee W.M. An Y.J. Yoon H. et al.: ‘Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): plant agar test for water‐insoluble nanoparticles’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2008, 27, (9), pp. 1915 –1921 - PubMed
-
- Lee C.W. Mahendra S. Zodrow K. et al.: ‘Developmental phytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana ’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2010, 29, (3), pp. 669 –675 - PubMed
-
- Dubchak S. Ogar A. Mietelski J.W. et al.: ‘Influence of silver and titanium nanoparticles on arbuscular mycorrhiza colonization and accumulation of radiocaesium in Helianthus annuus ’, Spanish J. Agric. Res., 2010, 8, (S1), pp. 103 –108
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

