Laser-induced heating for in situ DNA replication and detection in microchannels
- PMID: 30104460
- PMCID: PMC8676601
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0302
Laser-induced heating for in situ DNA replication and detection in microchannels
Abstract
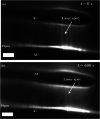
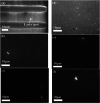
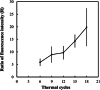
This study proposes a method for in situ local deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and detection in a long DNA strand through laser-induced heating and strong avidin-biotin binding. To achieve the target DNA replication, dielectrophoresis was generated to stretch and immobilise DNA strands on both ends of the electrode. Subsequently, local DNA sequences were replicated using thermal cycles generated by laser-induced heating. Replicated double-stranded DNA products were captured in situ on a solid surface and detected using the fluorescence intensity of quantum dots (Qdots). The results revealed that after six laser-induced thermal cycles, the replicated local DNA sequence could be detected by analysing the difference between Qdot fluorescent intensity before and after replication. The proposed method is expected to improve the efficiency of biosample gene sequence analysis.
Figures
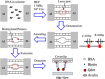
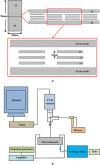
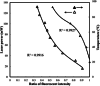

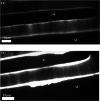

References
-
- Cao L. Cui X. Hu J. et al.: ‘Advances in digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) and its emerging biomedical applications’, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 90, pp. 459 –474 - PubMed
-
- Xia J. Su M.: ‘Chip‐scale alignment of long DNA nanofibers on a patterned self‐assembled monolayer’, Lab. Chip., 2017, 17, pp. 3234 –3239 - PubMed
-
- Hsieh Y.‐F. Yonezawa E Kuo L.‐S. et al.: ‘Polymerase chain reaction with phase change as intrinsic thermal control’, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102, p. 173701
-
- Hung M.‐S. Chen C.‐P.: ‘Laser‐induced heating for DNA replication in a microfluidics’, JPS Conf. Proc., 2014, 1, p. 012058
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

