Molecular Targets in Hepatocarcinogenesis and Implications for Therapy
- PMID: 30104473
- PMCID: PMC6112027
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm7080213
Molecular Targets in Hepatocarcinogenesis and Implications for Therapy
Abstract
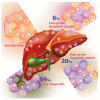
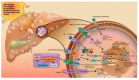
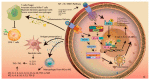
Hepatocarcinogenesis comprises of multiple, complex steps that occur after liver injury and usually involve several pathways, including telomere dysfunction, cell cycle, WNT/β-catenin signaling, oxidative stress and mitochondria dysfunction, autophagy, apoptosis, and AKT/mTOR signaling. Following liver injury, gene mutations, accumulation of oxidative stress, and local inflammation lead to cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and necrosis. The persistence of this vicious cycle in turn leads to further gene mutation and dysregulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13, IL-18, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, resulting in immune escape by means of the NF-κB and inflammasome signaling pathways. In this review, we summarize studies focusing on the roles of hepatocarcinogenesis and the immune system in liver cancer. In addition, we furnish an overview of recent basic and clinical studies to provide a strong foundation to develop novel anti-carcinogenesis targets for further treatment interventions.
Keywords: NF-κB; hepatocarcinogenesis; inflammasome; liver cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

