JASPAC: Japan Spastic Paraplegia Research Consortium
- PMID: 30104498
- PMCID: PMC6119894
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci8080153
JASPAC: Japan Spastic Paraplegia Research Consortium
Abstract
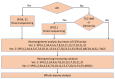
Hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSPs) are a group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by weakness and spasticity of the lower extremities. HSPs are heterogeneous disorders that involve over 80 causative genes. The frequency of HSPs is estimated to be 10⁻100/1,000,000. With this background, the Japanese research group "Japan Spastic Paraplegia Research Consortium: JASPAC" was organized in 2006 to elucidate the molecular epidemiologies of HSPs in Japan and the molecular pathologies of HSPs. To date, the JASPAC has collected 714 HSP families and analyzed 488 index patients. We found 279 pathogenic variants or probable pathogenic variants of causative genes in the 488 HSP patients. According to our results, we found 178 families with autosomal dominant patients (65%), and 101 with autosomal recessive and sporadic patients (48%). We found 119 patients with SPG4, 17 with SPG3A, 15 with SPG31, 13 with SPG11, and 11 with SPG10. Other HSP genes were the cause in less than five patients. On the other hand, we could not find causative genes in 35% of the autosomal dominant patients, or 52% of the autosomal recessive and sporadic patients. We are now trying to find new causative genes and elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying HSPs.
Keywords: JASPAC; SPG10; SPG31; SPG3A; SPG4; hereditary spastic paraplegias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hirayama K., Takayanagi T., Nakamura R., Yanagisawa N., Hattori T., Kita K., Yanagimoto S., Fujita M., Nagaoka M., Satomura Y., et al. Spinocerebellar degenerations in Japan: A nationwide epidemiological and clinical study. Acta Neuro. Scand. Suppl. 1994;153:1–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1994.tb05401.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shimazaki H., Takiyama Y., Ishiura H., Sakai C., Matsushima Y., Hatakeyama H., Honda J., Sakoe K., Naoi T., Namekawa M., et al. A homozygous mutation of C12orf65 causes spastic paraplegia with optic atrophy and neuropathy. J. Med. Genet. 2012;49:777–784. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101212. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

