Soybean- and Lupin-Derived Peptides Inhibit DPP-IV Activity on In Situ Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells and Ex Vivo Human Serum
- PMID: 30104520
- PMCID: PMC6115767
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10081082
Soybean- and Lupin-Derived Peptides Inhibit DPP-IV Activity on In Situ Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells and Ex Vivo Human Serum
Abstract
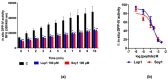
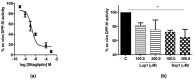
Recent investigations have focused on food-derived peptides as novel natural inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV), a new target for diabetes. This study aimed to optimize fast, sensitive, and cost-effective DPP-IV assays in situ on human intestinal Caco-2 cells and ex vivo on human serum. Both assays were applied to investigate the inhibitory activity of soy and lupin peptides. The best conditions for in situ DPP-IV activity in Caco-2 cells were obtained using 2-day cells and 50 µM Gly-Pro-AMC. Sitagliptin, used as reference inhibitor, showed a dose-dependent response with a 50% inhibition concentration (IC50) of 0.6 µM. A lower IC50 (0.2 µM) was obtained for sitagliptin on human serum incubated with the substrate for 24 h. Both assays were applied to assess the activity of Lup1 (LTFPGSAED) and Soy1 (IAVPTGVA) on DPP-IV. Lup1 and Soy1 inhibited DPP-IV in situ, with IC50 values of of 207.5 and 223.2 µM, respectively, and maintained their inhibitory activity ex vivo on circulating DPP-IV with a slightly lower potency. These assays can be used to characterize the DPP-IV inhibitory activity of food-derived molecules more accurately than in vitro biochemical tests. This combined approach also considers their effects on the circulating form of DPP-IV, correlated to metabolic diseases.
Keywords: anti-diabetic activity; bioactive peptides; dipeptidyl peptidase IV; glucose metabolism; sitagliptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
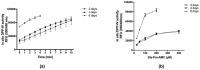

Similar articles
-
A Supramolecular Approach to Develop New Soybean and Lupin Peptide Nanogels with Enhanced Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Activity.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Apr 3;67(13):3615-3623. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b07264. Epub 2019 Mar 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30879293
-
Utilisation of the isobole methodology to study dietary peptide-drug and peptide-peptide interactive effects on dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibition.Food Funct. 2015 Jan;6(1):313-20. doi: 10.1039/c4fo00883a. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 25477187
-
Peptides Derived from Soy and Lupin Protein as Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors: In Vitro Biochemical Screening and in Silico Molecular Modeling Study.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Dec 28;64(51):9601-9606. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04041. Epub 2016 Dec 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27983830
-
Features of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from dietary proteins.J Food Biochem. 2019 Jan;43(1):e12451. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12451. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31353485 Review.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its inhibitors: therapeutics for type 2 diabetes and what else?J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 27;57(6):2197-212. doi: 10.1021/jm400658e. Epub 2013 Oct 24. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24099035 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo and In Vitro Comparison of the DPP-IV Inhibitory Potential of Food Proteins from Different Origins after Gastrointestinal Digestion.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8365. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158365. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955493 Free PMC article.
-
The Beneficial Effects of Soybean Proteins and Peptides on Chronic Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 7;15(8):1811. doi: 10.3390/nu15081811. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of the Stability and Anti-DPPIV Activity of Hempseed Hydrolysates Through Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Hydrogels.Front Chem. 2019 Jan 24;6:670. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00670. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 30733941 Free PMC article.
-
Phycobiliproteins from Arthrospira Platensis (Spirulina): A New Source of Peptides with Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Activity.Nutrients. 2020 Mar 18;12(3):794. doi: 10.3390/nu12030794. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32197331 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Hydrolysis of Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) Conglutins with Plant Proteases Releases Antihypertensive and Antidiabetic Peptides That Are Bioavailable, Non-Toxic, and Gastrointestinal Digestion Stable.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 29;25(23):12866. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312866. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lacroix I.M.E., Li-Chan E.C.Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity of dairy protein hydrolysates. Int. Dairy J. 2012;25:97–102. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2012.01.003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

