Effects of Rhizome Extract of Dioscorea batatas and Its Active Compound, Allantoin, on the Regulation of Myoblast Differentiation and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in C2C12 Myotubes
- PMID: 30104552
- PMCID: PMC6222821
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23082023
Effects of Rhizome Extract of Dioscorea batatas and Its Active Compound, Allantoin, on the Regulation of Myoblast Differentiation and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in C2C12 Myotubes
Abstract
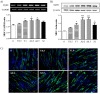
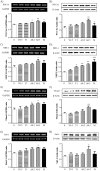
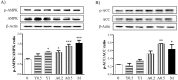
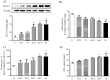
With the aging process, a loss of skeletal muscle mass and dysfunction related to metabolic syndrome is observed in older people. Yams are commonly use in functional foods and medications with various effects. The present study was conducted to investigate the effects of rhizome extract of Dioscorea batatas (Dioscoreae Rhizoma, Chinese yam) and its bioactive compound, allantoin, on myoblast differentiation and mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle cells. Yams were extracted in water and allantoin was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The expression of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) and mitochondrial biogenesis-regulating factors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), sirtuin-1 (Sirt-1), nuclear respiratory factor-1 (NRF-1) and transcription factor A, mitochondrial (TFAM), and the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) were determined in C2C12 myotubes by reverse transcriptase (RT)-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or western blot. The glucose levels and total ATP contents were measured by glucose consumption, glucose uptake and ATP assays, respectively. Treatment with yam extract (1 mg/mL) and allantoin (0.2 and 0.5 mM) significantly increased MyHC expression compared with non-treated myotubes. Yam extract and allantoin significantly increased the expression of PGC-1α, Sirt-1, NRF-1 and TFAM, as well as the phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC in C2C12 myotubes. Furthermore, yam extract and allantoin significantly increased glucose uptake levels and ATP contents. Finally, HPLC analysis revealed that the yam water extract contained 1.53% of allantoin. Yam extract and allantoin stimulated myoblast differentiation into myotubes and increased energy production through the upregulation of mitochondrial biogenesis regulators. These findings indicate that yam extract and allantoin can help to prevent skeletal muscle dysfunction through the stimulation of the energy metabolism.
Keywords: C2C12 cells; Chinese yam; Dioscorea batatas; Dioscoreae Rhizoma; allantoin; mitochondrial biogenesis; myoblast differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory effects of the fruit extract of Lycium chinense and its active compound, betaine, on muscle differentiation and mitochondrial biogenesis in C2C12 cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109297. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109297. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31404771
-
Effects of a rhizome aqueous extract of Dioscorea batatas and its bioactive compound, allantoin in high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and the regulation of liver, pancreas and skeletal muscle dysfunction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;259:112926. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112926. Epub 2020 May 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32380247
-
Saururus chinensis (Lour.) Baill. extract promotes skeletal muscle cell differentiation by positively regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and AKT/mTOR signaling in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jul;30(1):125. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13250. Epub 2024 May 24. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38785149 Free PMC article.
-
Research and Development of Proteins and Peptides with Therapeutic Potential from Yam Tubers.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(3):277-284. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180622094356. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019. PMID: 29932033 Review.
-
Advanced Studies on Rhizoma Dioscoreae Collettii.Chin J Integr Med. 2020 Mar;26(3):235-240. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2263-1. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 27286710 Review.
Cited by
-
Allantoin reduces glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity in a type 2 diabetes rat model by modulating the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 18;10(15):e34716. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34716. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39144993 Free PMC article.
-
Decapeptide from Potato Hydrolysate Induces Myogenic Differentiation and Ameliorates High Glucose-Associated Modulations in Protein Synthesis and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in C2C12 Cells.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 11;12(4):565. doi: 10.3390/biom12040565. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454154 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids: nutraceutical potential for counteracting muscle atrophy.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2020 Sep 16;29(12):1619-1640. doi: 10.1007/s10068-020-00816-5. eCollection 2020 Dec. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33282430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constituents of Huberantha jenkinsii and Their Biological Activities.Molecules. 2020 Aug 2;25(15):3533. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153533. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32748832 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity of a Dioscorea Rhizome water extract.Toxicol Res. 2021 Jan 2;37(3):385-393. doi: 10.1007/s43188-020-00077-8. eCollection 2021 Jul. Toxicol Res. 2021. PMID: 34295802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pyla R., Pichavaram P., Fairaq A., Park M.A., Kozak M., Kamath V., Patel V.S., Segar L. Altered energy state reversibly controls smooth muscle contractile function in human saphenous vein during acute hypoxia-reoxygenation: Role of glycogen, AMP-activated protein kinase, and insulin-independent glucose uptake. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015;97:77–88. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim I.R., Kim H.C., Kook Y.B., Park S.J., Park Y.K., Park J.H., Seo B.I., Seo Y.B., Song H.J., Shin M.K., et al. Herbology. Yonglims; Seoul, Korea: 2007. pp. 580–581.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

