Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit
- PMID: 3010466
- PMCID: PMC4451858
- DOI: 10.1126/science.3010466
Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit
Abstract
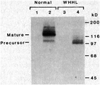
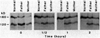
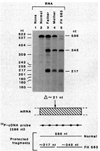
The Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic (WHHL) rabbit, an animal with familial hypercholesterolemia, produces a mutant receptor for plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL) that is not transported to the cell surface at a normal rate. Cloning and sequencing of complementary DNA's from normal and WHHL rabbits, shows that this defect arises from an in-frame deletion of 12 nucleotides that eliminates four amino acids from the cysteine-rich ligand binding domain of the LDL receptor. A similar mutation, detected by S1 nuclease mapping of LDL receptor messenger RNA, occurred in a patient with familial hypercholesterolemia whose receptor also fails to be transported to the cell surface. These findings suggest that animal cells may have fail-safe mechanisms that prevent the surface expression of improperly folded proteins with unpaired or improperly bonded cysteine residues.
Figures







References
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. In: in The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. 5. Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Fredrickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, editors. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1983. pp. 672–712.
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Anderson RGW, Russell DW, Schneider WJ. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1985;1:1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

