Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism
- PMID: 30104701
- PMCID: PMC6380503
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-018-0044-8
Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism
Abstract
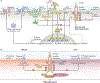
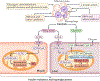
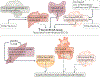
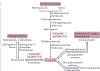
The cause of insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is not limited to impaired insulin signalling but also involves the complex interplay of multiple metabolic pathways. The analysis of large data sets generated by metabolomics and lipidomics has shed new light on the roles of metabolites such as lipids, amino acids and bile acids in modulating insulin sensitivity. Metabolites can regulate insulin sensitivity directly by modulating components of the insulin signalling pathway, such as insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) and AKT, and indirectly by altering the flux of substrates through multiple metabolic pathways, including lipogenesis, lipid oxidation, protein synthesis and degradation and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Moreover, the post-translational modification of proteins by metabolites and lipids, including acetylation and palmitoylation, can alter protein function. Furthermore, the role of the microbiota in regulating substrate metabolism and insulin sensitivity is unfolding. In this Review, we discuss the emerging roles of metabolites in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and T2DM. A comprehensive understanding of the metabolic adaptations involved in insulin resistance may enable the identification of novel targets for improving insulin sensitivity and preventing, and treating, T2DM.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
B.B.K. is an inventor on patents related to the fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
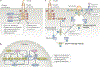
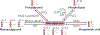
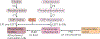
References
-
- Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B & Kahn CR Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 7, 85–96 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, Gulluni F & Hirsch E PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann. Med 46, 372–383 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Wymann MP & Schneiter R Lipid signalling in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 9, 162–176 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

