Differential expression of miRNA199b-5p as a novel biomarker for sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors
- PMID: 30104706
- PMCID: PMC6089933
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30484-9
Differential expression of miRNA199b-5p as a novel biomarker for sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors
Abstract
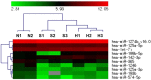
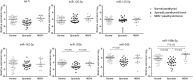
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are dysregulated in many tumors; however, miRNA regulation in parathyroid tumors remains poorly understood. To identify differentially expressed miRNAs between sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors and to analyze their correlation with clinicopathological features, a microarray containing 887 miRNAs was performed; then, the differentially expressed miRNAs were validated by qRT-PCR using 25 sporadic and 12 hereditary parathyroid tumors and 24 normal parathyroid tissue samples. A receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was applied to evaluate the utility of the miRNAs for distinguishing parathyroid tumor types. Compared to the miRNAs in the normal parathyroid tissues, 10 miRNAs were differentially expressed between the sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors. Seven of these miRNAs (let-7i, miR-365, miR-125a-3p, miR-125a-5p, miR-142-3p, miR-193b, and miR-199b-5p) were validated in the parathyroid tumor samples. Among these miRNAs, only miR-199b-5p was differentially expressed (P < 0.001); miR-199b-5p was significantly downregulated and negatively associated with PTH levels (γ = -0.579, P = 0.002) in the sporadic tumors but was upregulated in the hereditary tumors. This miRNA showed 67% sensitivity and 100% specificity for distinguishing sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors. These results reveal altered expression of a miRNA between sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors and the potential role of miR-199b-5p as a novel biomarker for distinguishing these two types of parathyroid tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential expression profiles of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jun;37(6):3543-3553. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5612. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28498428
-
Identification of differentially expressed microRNA in parathyroid tumors.Ann Surg Oncol. 2011 Apr;18(4):1158-65. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-1359-7. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21086055 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed miR-3680-5p is associated with parathyroid hormone regulation in peritoneal dialysis patients.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 2;12(2):e0170535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170535. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28152049 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNA Expression Profiling in Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 15;9:856358. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.856358. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35783849 Free PMC article.
-
Interactome of PTH-Regulated miRNAs and Their Predicted Target Genes for Investigating the Epigenetic Effects of PTH (1-34) in Bone Metabolism.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 13;13(8):1443. doi: 10.3390/genes13081443. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Usefulness of serum microRNA as a predictive marker of recurrence and prognosis in biliary tract cancer after radical surgery.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 11;9(1):5925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42392-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30976046 Free PMC article.
-
[Plasma miRNA expression in patients with genetically confirmed multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 syndrome and its phenocopies].Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 2024 Jan 24;69(6):70-85. doi: 10.14341/probl13357. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 2024. PMID: 38311997 Free PMC article. Russian.
-
MicroRNA‑199a/b‑5p inhibits endometrial cancer cell metastasis and invasion by targeting FAM83B in the epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):304. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11943. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649801 Free PMC article.
-
Serums miR-24-3p and miR-1301-3p as Potential Biomarkers in MEN1 Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 24;26(11):5076. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115076. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507887 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Signaling Pathways and Epigenetic Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):1331. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021331. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeLellis RA, Mazzaglia P, Mangray S. Primary hyperparathyroidism: a current perspective. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132:1251–1262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

