Extremely high levels of vancomycin can cause severe renal toxicity
- PMID: 30104890
- PMCID: PMC6071627
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S171669
Extremely high levels of vancomycin can cause severe renal toxicity
Abstract
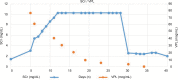
Vancomycin has usually been associated with nephrotoxicity. Generally, this toxicity is presented as proximal tubular cells injury with or without necrosis and as acute interstitial nephritis. However, development of both lesions is uncommonly described in literature. We present a case of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity resulting in both acute interstitial nephritis and tubular cells damage confirmed by renal biopsy. Peak and trough levels of 77.11 and 63.60 μg/mL, respectively, were obtained at the first plasma determination. After 8 more plasma determinations and several hemodialysis sessions, vancomycin levels were undetectable 1 month after therapy was stopped. To our knowledge, this is the case report with the highest vancomycin trough levels developing both lesions and describing total vancomycin washout after a biopsy-proven vancomycin toxicity. In conclusion, early vancomycin therapeutic drug monitoring should be performed in order to avoid toxicities where, as seen in our patient, antibiotic exposure could last around 1 month after last dose administration.
Keywords: nephrotoxicity; therapeutic drug monitoring; vancomycin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Vancomycin trough level and loading dose.Infect Drug Resist. 2018 Nov 23;11:2393-2396. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S184897. eCollection 2018. Infect Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 30538506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rybak M, Lomaestro B, Rotschafer JC, et al. Therapeutic Monitoring of Vancomycin in Adult Patients: A Consensus Review of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Heal Pharm. 2009;66:82–98. - PubMed
-
- Gelfand MS, Cleveland KO, Mazumder SA. Vancomycin-induced interstitial nephritis superimposed on coexisting renal disease: the importance of renal biopsy. Am J Med Sci. 2014;347(4):338–340. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources