Burden and risk factors of diabetes and hyperglycemia in India: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
- PMID: 30104893
- PMCID: PMC6074770
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S157376
Burden and risk factors of diabetes and hyperglycemia in India: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
Abstract
Background: Diabetes, hyperglycemia, and their complications are a growing problem in India. However, no comprehensive picture of this disease burden has yet been presented to date.
Methods: I used aggregate data from the Global Burden of Disease 2016 to describe the burden of diabetes and its risk factors, chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to diabetes, and diseases caused by high fasting plasma glucose from 1990 to 2016 in India.
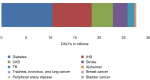
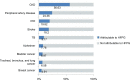
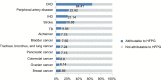
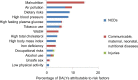
Results: Deaths due to diabetes accounted for 3.1% (95% uncertainty interval [UI]: 2.9-3.3) of all deaths in India in 2016, up from 0.98% (95% UI: 0.87-1.1) of all deaths in 1990. Diabetes and hyperglycemia accounted for 27.5 million disability-adjusted life years in 2016, of which diabetes accounted for 10 million. Diabetes contributes to the causation of ischemic heart disease, stroke, CKD, peripheral artery disease, specific cancers, and tuberculosis via intermediate hyperglycemia. High body mass index, dietary factors (diet low in fruits, nuts and seeds, and whole grains), and tobacco use were the most important risk factors for diabetes.
Conclusion: Diabetes and CKD due to hyperglycemia pose a large and increasing burden in India. Urgent programs and policies are needed to reduce the identified risk factors for diabetes and its burden.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; diabetes; hyperglycemia; ischemic heart disease; morbidity; mortality; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas - 8th edition. [Accessed June 13, 2018]. Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation GBD Compare | Viz Hub. 2017. [Accessed November 13, 2017]. Available from: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/
-
- Moradi-Lakeh M, Forouzanfar MH, El Bcheraoui C, et al. High fasting plasma glucose, diabetes, and its risk factors in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 1990–2013: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):22–29. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2016 DALYs and HALE Collaborators Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1260–1344. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

