Intercepting signalling mechanism to control environmental biofouling
- PMID: 30105189
- PMCID: PMC6085211
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-018-1383-z
Intercepting signalling mechanism to control environmental biofouling
Abstract
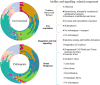
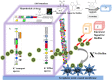
Biofouling in environmental systems employs bacterial quorum sensing signals (autoinducers) and extracellular polymeric substances to onset the event. The present review has highlighted on the fundamental mechanisms behind biofilm formation over broad spectrum environmental niches especially membrane biofouling in water systems and consequent chances of pathogenic contamination leading to global economic loss. It has broadly discussed on bioelectrical signal (via, potassium gradient) and molecular signal (via, AHLs) mediated quorum sensing which help to propagate biofilm formation. The review has illustrated the potential of genomic intervention towards biofouled membrane microbial community and has uncovered possible features of biofilm microenvironment like quorum quenching bacteria, bioelectrical waves capture, siderophores arrest and surface modifications. Based on information, the concept of interception of quorum signals (AHLs) and bioelectrical signals (K+) by employing electro-modified (negative charges) membrane surface have been hypothesized in the present review to favour anti-biofouling.
Keywords: Bioelectrical wave; Genomic; Membrane biofouling; Quorum sensing; Siderophore.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsAll the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Microbial population dynamics and proteomics in membrane bioreactors with enzymatic quorum quenching.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 May;97(10):4665-75. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4272-0. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22846900
-
Control of indigenous quorum quenching bacteria on membrane biofouling in a short-period MBR.Bioresour Technol. 2019 Jul;283:261-269. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.082. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Bioresour Technol. 2019. PMID: 30913434
-
Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: physical and biological effects.Environ Sci Technol. 2013 Jan 15;47(2):836-42. doi: 10.1021/es303995s. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Environ Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 23256502
-
Process-Oriented Review of Bacterial Quorum Quenching for Membrane Biofouling Mitigation in Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs).Membranes (Basel). 2016 Dec 13;6(4):52. doi: 10.3390/membranes6040052. Membranes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27983578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum quenching enzymes.J Biotechnol. 2015 May 10;201:2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 16. J Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25220028 Review.
Cited by
-
D-Tryptophan governs biofilm formation rates and bacterial interaction in P. mendocina and S. aureus.J Biosci. 2019 Mar;44(1):3. J Biosci. 2019. PMID: 30837355
References
-
- Araújo PA, Kruithof JC, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Vrouwenvelder JS. The potential of stard modified feed spacers for biofouling control. J MemSci. 2012;403:58–70.
-
- Bengtsson MM, Sjøtun K, Øvreås L. Seasonal dynamics of bacterial biofilms on the kelp Laminaria hyperborean. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2010
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

