C‑C chemokine receptor type 3 gene knockout alleviates inflammatory responses in allergic rhinitis model mice by regulating the expression of eosinophil granule proteins and immune factors
- PMID: 30106146
- PMCID: PMC6131541
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9380
C‑C chemokine receptor type 3 gene knockout alleviates inflammatory responses in allergic rhinitis model mice by regulating the expression of eosinophil granule proteins and immune factors
Abstract
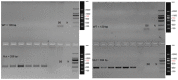
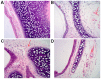
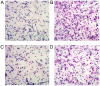
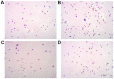
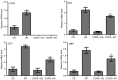
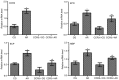
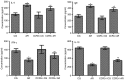
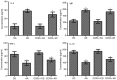
The present study aimed to investigate the effects of C‑C chemokine receptor type 3 (CCR3) gene knockout on allergic rhinitis (AR) in mice, as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms. Ovalbumin was administrated to CCR3+/+ and CCR3‑/‑ BALB/c mice to establish an AR model. The mice were divided into four groups: i) Normal control (CG), ii) AR model (AR), iii) CCR3 knockout CG (CCR3‑/‑CG) and iv) AR model with CCR3 knockout (CCR3‑/‑AR). Histological sections of nasal mucosae were examined by hematoxylin and eosin staining, which revealed that CCR3 knockout suppressed the invasion of inflammatory cells and relieved the damage of nasal mucosae. Peripheral blood smear and nasal‑washing smears were evaluated by Wright's staining. Eosinophil (EOS) numbers in nasal mucosae, peripheral blood, and nasal washings of the various groups were ranked in the order: AR>CCR3‑/‑AR>CG>CCR3‑/‑. mRNA expression levels of CCR3, EOS peroxidase (EPO), EOS cationic protein (ECP), and major basic protein (MBP) in the peripheral serum and nasal washings were detected by reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction. Interferon‑γ (IFN‑γ), interleukin (IL)‑4, IL‑10, and immunoglobulin E (IgE) protein levels in the peripheral serum and nasal washings were investigated by ELISA. CCR3 mRNA expression was not detected in the CCR3‑/‑ and CCR3‑/‑AR groups, whereas expression levels in the AR group were markedly higher compared with expression in the CG group. Compared with the CG‑associated groups (i.e., the CG and CCR3‑/‑CG groups), the levels of EPO, ECP, MBP, IL‑4, and IgE were significantly increased in the AR‑associated groups (that is, R and CCR3‑/‑AR). In addition, the CCR3‑/‑AR group mice produced significantly lower levels of EPO, ECP, MBP, IL‑4 and IgE compared with the AR group, whereas the expression levels of IFN‑γ and IL‑10 were increased. CCR3 gene knockout may alleviate EOS invasion and the inflammatory response in AR model mice by reducing the expression levels of EPO, ECP, MBP, IL‑4, and IgE, and increasing the expression of IL‑10 and IFN‑γ.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of CCR3 gene on related inflammatory cells in respiratory allergic diseases].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jan 5;35(1):80-84. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.01.021. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33540982 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Effects of lentivirus-mediated CCR3 RNA interference on the function of mast cells of allergic rhinitis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:106011. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106011. Epub 2019 Nov 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31776094
-
Effect of RNA interference therapy on the mice eosinophils CCR3 gene and granule protein in the murine model of allergic rhinitis.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014 Mar;7(3):226-30. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60026-2. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014. PMID: 24507645
-
CCR3 gene knockout in bone marrow cells ameliorates combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) by reducing airway inflammatory cell infiltration and Th2 cytokines expression in mice model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Mar;104:108509. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108509. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34998035
-
The Role of Neuro-Immune Interactions in the Pathology and Pathogenesis of Allergic Rhinitis.Immunol Invest. 2024 Oct;53(7):1013-1029. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2024.2382792. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Immunol Invest. 2024. PMID: 39042045 Review.
Cited by
-
[Diagnostic value of a novel test paper detection of ECP in nasal secretion for allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;36(6):407-413. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.001. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35822356 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma.Open Life Sci. 2023 Dec 7;18(1):20220779. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0779. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 38077793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effect of CCR3 gene on related inflammatory cells in respiratory allergic diseases].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jan 5;35(1):80-84. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.01.021. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33540982 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
CCL22 induces pro-inflammatory changes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes.iScience. 2020 Dec 13;24(1):101943. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101943. eCollection 2021 Jan 22. iScience. 2020. PMID: 33490888 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

