Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus are distinct diseases with potential overlapping metabolic dysfunction upstream of observed cognitive decline
- PMID: 30106209
- PMCID: PMC6427919
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.12655
Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus are distinct diseases with potential overlapping metabolic dysfunction upstream of observed cognitive decline
Abstract
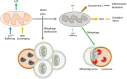
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are highly prevalent aging-related diseases associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Some findings in human and animal models have linked T2DM to AD-type dementia. Despite epidemiological associations between the T2DM and cognitive impairment, the interrelational mechanisms are unclear. The preponderance of evidence in longitudinal studies with autopsy confirmation have indicated that vascular mechanisms, rather than classic AD-type pathologies, underlie the cognitive decline often seen in self-reported T2DM. T2DM is associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease (CVD), and is associated with increased risk of infarcts and small vessel disease in the brain and other organs. Neuropathological examinations of post-mortem brains demonstrated evidence of cerebrovascular disease and little to no correlation between T2DM and β-amyloid deposits or neurofibrillary tangles. Nevertheless, the mechanisms upstream of early AD-specific pathology remain obscure. In this regard, there may indeed be overlap between the pathologic mechanisms of T2DM/"metabolic syndrome," and AD. More specifically, cerebral insulin processing, glucose metabolism, mitochondrial function, and/or lipid metabolism could be altered in patients in early AD and directly influence symptomatology and/or neuropathology.
Keywords: VCID; epidemiology; mitochondria; neuropathology; pathogenesis; preclinical.
© 2018 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Tale of Two Diseases: Exploring Mechanisms Linking Diabetes Mellitus with Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85(2):485-501. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210612. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 34842187 Review.
-
Impaired cerebral blood flow in type 2 diabetes mellitus - A comparative study with subjective cognitive decline, vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease subjects.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102302. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102302. Epub 2020 May 28. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32521474 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic perspective of astrocyte dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes brains.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114206. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114206. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36916433 Review.
-
The overlap between vascular disease and Alzheimer's disease--lessons from pathology.BMC Med. 2014 Nov 11;12:206. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0206-2. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 25385447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Alzheimer's disease from perturbed cerebral glucose metabolism: implications for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Sep;108:21-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23850509 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Nonlipogenic ABCA1 Inducing Compounds with Potential in Alzheimer's Disease and Type 2 Diabetes.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 Jan 5;4(1):143-154. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00149. eCollection 2021 Feb 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33615168 Free PMC article.
-
Biological sex and DNA repair deficiency drive Alzheimer's disease via systemic metabolic remodeling and brain mitochondrial dysfunction.Acta Neuropathol. 2020 Jul;140(1):25-47. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02152-8. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Acta Neuropathol. 2020. PMID: 32333098 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the liver in dementia and cognitive impairment: Dietary macronutrients and diabetic therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Nov;190:114537. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114537. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 36115494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the Role of Isoeugenol from Ocimum tenuiflorum against Diabetes Mellitus-Linked Alzheimer's Disease through Network Pharmacology and Computational Methods.Molecules. 2022 Apr 7;27(8):2398. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082398. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458596 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of cognitive flexibility in type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Oct 3;371:111978. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111978. Epub 2019 May 26. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31141724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahtiluoto S, Polvikoski T, Peltonen M, Solomon A, Tuomilehto J, Winblad B et al (2010 Sep 28) Diabetes, Alzheimer disease, and vascular dementia: a population‐based neuropathologic study. Neurology 75:1195–1202. - PubMed
-
- Akai K, Uchigasaki S, Tanaka U, Komatsu A (1987 Jan) Normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neuropathological study. Acta Pathol Jpn 37:97–110. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR (1995) An English translation of Alzheimer's 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat 8:429–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

