The adhesion function of the sodium channel beta subunit (β1) contributes to cardiac action potential propagation
- PMID: 30106376
- PMCID: PMC6122953
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.37610
The adhesion function of the sodium channel beta subunit (β1) contributes to cardiac action potential propagation
Abstract
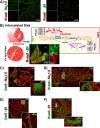
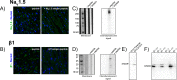
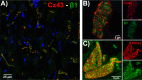
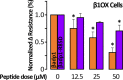
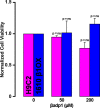
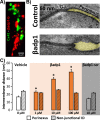
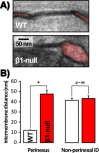
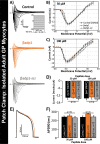
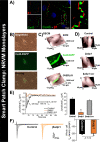
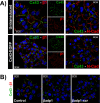
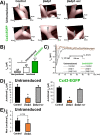
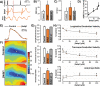
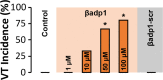
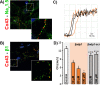
Computational modeling indicates that cardiac conduction may involve ephaptic coupling - intercellular communication involving electrochemical signaling across narrow extracellular clefts between cardiomyocytes. We hypothesized that β1(SCN1B) -mediated adhesion scaffolds trans-activating NaV1.5 (SCN5A) channels within narrow (<30 nm) perinexal clefts adjacent to gap junctions (GJs), facilitating ephaptic coupling. Super-resolution imaging indicated preferential β1 localization at the perinexus, where it co-locates with NaV1.5. Smart patch clamp (SPC) indicated greater sodium current density (INa) at perinexi, relative to non-junctional sites. A novel, rationally designed peptide, βadp1, potently and selectively inhibited β1-mediated adhesion, in electric cell-substrate impedance sensing studies. βadp1 significantly widened perinexi in guinea pig ventricles, and selectively reduced perinexal INa, but not whole cell INa, in myocyte monolayers. In optical mapping studies, βadp1 precipitated arrhythmogenic conduction slowing. In summary, β1-mediated adhesion at the perinexus facilitates action potential propagation between cardiomyocytes, and may represent a novel target for anti-arrhythmic therapies.
Keywords: apahptic coupling; arrhythmia; cardiac conduction; cell biology; gap junctions; guinea pig.
© 2018, Veeraraghavan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RV, GH, AA, DH, XW, DK, JS, CC, JJ, LI, ID, JS, JG, SP, RG No competing interests declared
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL132236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/17/13/33173/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL141855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056728/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RO1 HL HL141855-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RO1 HL56728-15A2/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102298-01A1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102298-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37NS076752/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 16SDG29870007/American Heart Association/International
- R01 HL102298/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS076752/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

