4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole Distinctly Labels Tau Deposits
- PMID: 30106598
- PMCID: PMC6158628
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155418793600
4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole Distinctly Labels Tau Deposits
Abstract
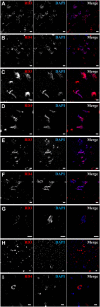
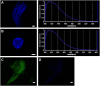
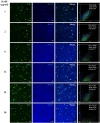
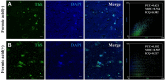
Tau deposits have distinct biochemical characteristics and vary morphologically based on identification with tau antibodies and several chemical dyes. Here, we report 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-positivity of tau deposits. Furthermore, we investigated the cause for this positivity. DAPI was positive in 3R/4R (3-repeat/4-repeat) tau deposits in Alzheimer's disease, myotonic dystrophy, and neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation, and in 4R tau deposits in corticobasal degeneration, but negative in 4R tau deposits in frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-17 and progressive supranuclear palsy. The peak emission wavelength of DAPI after binding to a tau deposit was similar to that after binding to a nucleus. This DAPI-positivity was conspicuous at the optimum concentration of 2 μg/ml. DAPI-positivity was diminished after formic acid treatment, but preserved after nucleic acid elimination and phosphate moiety blocking. Our results suggest that staining with 2 μg/ml DAPI is a common but useful tool to differentially detect tau deposits in various tauopathies.
Keywords: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Phos-tag; neurofibrillary tangle; tauopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Ferrer I, López-González I, Carmona M, et al. Glial and neuronal tau pathology in tauopathies: characterization of disease-specific phenotypes and tau pathology progression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014;73(1):81–97. - PubMed
-
- Mackenzie IRA. Neuropathology of atypical parkinsonian disorder. In: Litvan I, editor. Atypical parkinsonian disorders: clinical and research aspects. Current clinical neurology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2005:47–77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

