UBXN2A enhances CHIP-mediated proteasomal degradation of oncoprotein mortalin-2 in cancer cells
- PMID: 30107089
- PMCID: PMC6166003
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12372
UBXN2A enhances CHIP-mediated proteasomal degradation of oncoprotein mortalin-2 in cancer cells
Abstract
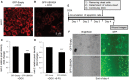
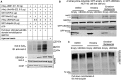
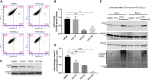
Overexpression of oncoproteins is a major cause of treatment failure using current chemotherapeutic drugs. Drug-induced degradation of oncoproteins is feasible and can improve clinical outcomes in diverse types of cancers. Mortalin-2 (mot-2) is a dominant oncoprotein in several tumors, including colorectal cancer (CRC). In addition to inactivating the p53 tumor suppressor protein, mot-2 enhances tumor cell invasion and migration. Thus, mot-2 is considered a potential therapeutic target in several cancer types. The current study investigated the biological role of a ubiquitin-like protein called UBXN2A in the regulation of mot-2 turnover. An orthogonal ubiquitin transfer technology followed by immunoprecipitation, in vitro ubiquitination, and Magnetic Beads TUBE2 pull-down experiments revealed that UBXN2A promotes carboxyl terminus of the HSP70-interacting protein (CHIP)-dependent ubiquitination of mot-2. We subsequently showed that UBXN2A increases proteasomal degradation of mot-2. A subcellular compartmentalization experiment revealed that induced UBXN2A decreases the level of mot-2 and its chaperone partner, HSP60. Pharmacological upregulation of UBXN2A using a small molecule, veratridine (VTD), decreases the level of mot-2 in cancer cells. Consistent with the in vitro results, UBXN2A+/- mice exhibited selective elevation of mot-2 in colon tissues. An in vitro Anti-K48 TUBE isolation approach showed that recombinant UBXN2A enhances proteasomal degradation of mot-2 in mouse colon tissues. Finally, we observed enhanced association of CHIP with the UBXN2A-mot-2 complex in tumors in an azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced mouse CRC model. The existence of a multiprotein complex containing UBXN2A, CHIP, and mot-2 suggests a synergistic tumor suppressor activity of UBXN2A and CHIP in mot-2-enriched tumors. This finding validates the UBXN2A-CHIP axis as a novel and potential therapeutic target in CRC.
Keywords: CHIP E3 ligase; UBXN2A; colorectal cancer; mortalin-2; mouse; veratridine.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Agsteribbe E, Huckriede A, Veenhuis M, Ruiters MH, Niezen‐Koning KE, Skjeldal OH, Skullerud K, Gupta RS, Hallberg R, van Diggelen OP et al (1993) A fatal, systemic mitochondrial disease with decreased mitochondrial enzyme activities, abnormal ultrastructure of the mitochondria and deficiency of heat shock protein 60. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193, 146–154. - PubMed
-
- Ando K, Oki E, Zhao Y, Ikawa‐Yoshida A, Kitao H, Saeki H, Kimura Y, Ida S, Morita M, Kusumoto T et al (2013) Mortalin is a prognostic factor of gastric cancer with normal p53 function. Gastric Cancer 17, 255–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

