The Parkinson's disease gene product DJ-1 modulates miR-221 to promote neuronal survival against oxidative stress
- PMID: 30107296
- PMCID: PMC6092527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.021
The Parkinson's disease gene product DJ-1 modulates miR-221 to promote neuronal survival against oxidative stress
Abstract
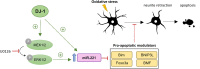
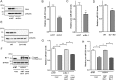
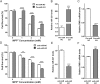
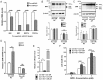
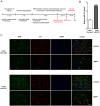
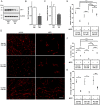
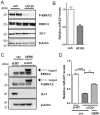
DJ-1 is a highly conserved protein that protects neurons against oxidative stress and whose loss of function mutations are linked to recessively inherited Parkinson's disease (PD). While a number of signaling pathways have been shown to be regulated by DJ-1, its role in controlling cell survival through non-coding RNAs remains poorly understood. Here, using a microarray screen, we found that knocking down DJ-1 in human neuroblastoma cells results in down-regulation of microRNA-221 (miR-221). This is one of the most abundant miRNAs in the human brain and promotes neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation. Yet the molecular mechanism linking miR-221 to genetic forms of PD has not been studied. Consistent with the microarray data, miR-221 expression is also decreased in DJ-1-/- mouse brains. Re-introduction of wild-type DJ-1, but not its PD-linked pathogenic M26I mutant, restores miR-221 expression. Notably, over-expression of miR-221 is protective against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-induced cell death, while inhibition of endogenous miR-221 sensitizes cells to this toxin. Additionally, miR-221 down-regulates the expression of several pro-apoptotic proteins at basal conditions and prevents oxidative stress-induced up-regulation of bcl-2-like protein 11 (BIM). Accordingly, miR-221 protects differentiated DJ-1 knock-down ReNcell VM human dopaminergic neuronal cells from MPP+-induced neurite retraction and cell death. DJ-1 is a known activator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and may modulate miR-221 levels in part through this pathway. We found that inhibiting ERK1/2 decreases miR-221 levels, whereas over-expressing ERK1 in DJ-1 knock-down cells increases miR-221 levels. These findings point to a new cytoprotective mechanism by which DJ-1 may increase miR-221 expression through the MAPK/ERK pathway, subsequently leading to repression of apoptotic molecules. The inability of a pathogenic DJ-1 mutant to modulate miR-221 further supports the relevance of this mechanism in neuronal health and its failure in DJ-1-linked PD.
Keywords: Autosomal recessive; DJ-1; Oxidative stress; PARK7; Parkinson's disease; miR-221; microRNA (miRNA).
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bonifati V., Rizzu P., van Baren M.J., Schaap O., Breedveld G.J., Krieger E., Dekker M.C., Squitieri F., Ibanez P., Joosse M., van Dongen J.W., Vanacore N., van Swieten J.C., Brice A., Meco G., van Duijn C.M., Oostra B.A., Heutink P. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science. 2003;299:256–259. - PubMed
-
- Bandopadhyay R., Kingsbury A.E., Cookson M.R., Reid A.R., Evans I.M., Hope A.D., Pittman A.M., Lashley T., Canet-Aviles R., Miller D.W., McLendon C., Strand C., Leonard A.J., Abou-Sleiman P.M., Healy D.G., Ariga H., Wood N.W., de Silva R., Revesz T., Hardy J.A., Lees A.J. The expression of DJ-1 (PARK7) in normal human CNS and idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Brain: J. Neurol. 2004;127:420–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

