Ketamine augmentation for major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation: Preliminary experience in an inpatient psychiatry setting
- PMID: 30107350
- PMCID: PMC6996199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.07.073
Ketamine augmentation for major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation: Preliminary experience in an inpatient psychiatry setting
Abstract
Background: Ketamine is known to rapidly reduce depressive symptoms and suicidal ideation (SI) in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), but evidence is limited for its acceptability and effectiveness in "real-world" settings. This case series examines serial ketamine infusions in reducing SI and depression scores in adults with MDD admitted to a tertiary care hospital.
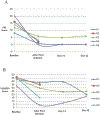
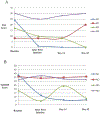
Methods: Five inpatients with MDD and SI admitted to hospital in Toronto, Canada received six infusions of 0.5 mg/kg intravenous (IV) ketamine (n = 5) over approximately 12 days, in addition to treatment-as-usual. Suicide and depression rating scores (Scale for Suicidal Ideation, SSI; Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, MADRS) were obtained at baseline, on treatment days, on days 14 and 42 (primary endpoint).
Results: All patients experienced benefit with ketamine. SSI scores diminished by 84% from 14.0 ± 4.5 at baseline to 2.2 ± 2.5 at study endpoint. MADRS scores diminished by 47% from 42.2 ± 5.3 at baseline to 22.4 ± 8.0. Two patients withdrew from the study, one to initiate electroconvulsive therapy and one due to an adverse event (dissociative effects) during the ketamine infusion.
Limitations: The major limitation of this study is the small sample size.
Discussion: These preliminary pilot data are promising with a greater than two-fold reduction in SI following ketamine infusions. They demonstrate that six serial ketamine infusions may be safe and feasible. These findings support the need for large scale randomized controlled trials to confirm the efficacy of serial ketamine for treatment of SI in "real-world" settings.
Keywords: Inpatients; Ketamine; Major depressive disorder; Midazolam; Suicide.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosures
Dr. Zarate is listed as a coinventor on a patent for the use of ketamine in major depression and suicidal ideation. Dr. Zarate is listed as a co-inventor on a patent for the use of (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine, (
Figures

References
-
- Ballard ED, Ionescu DF, Vande Voort JL, Niciu MJ, Richards EM, Luckenbaugh DA, Brutsché NE, Ameli R, Furey ML, Zarate CA Jr, 2014. Improvement in suicidal ideation after ketamine infusion: relationship to reductions in depression and anxiety. J Psychiatr. Res 58, 161–166. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.07.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Kovacs M, Weissman A, 1979. Assessment of suicidal intention: the scale for suicide ideation. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol 47 (2), 343–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

