The Effects of Add-on Fronto-Temporal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) on Auditory Verbal Hallucinations, Other Psychopathological Symptoms, and Insight in Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 30107404
- PMCID: PMC6209860
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy074
The Effects of Add-on Fronto-Temporal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) on Auditory Verbal Hallucinations, Other Psychopathological Symptoms, and Insight in Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of fronto-temporal transcranial direct current stimulation in treating auditory verbal hallucinations and other psychopathological symptoms of schizophrenia patients has been examined in a small number of clinical trials with limited sample sizes, but the results are mixed. Fronto-temporal transcranial direct current stimulation has also been demonstrated to enhance patients' insight into their mental illness in an open-label pilot study. The current investigation aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of fronto-temporal transcranial direct current stimulation on the severity of auditory verbal hallucinations, other schizophrenia symptoms, and insight in a large double blind, randomized, sham-controlled trial.
Methods: Sixty patients with medication-refractory auditory verbal hallucinations were randomized over 2 conditions: transcranial direct current stimulation with 2-mA, twice-daily sessions for 5 consecutive days, with anodal stimulation to the left prefrontal cortex and cathodal stimulation to the left temporo-parietal junction, and sham treatment.
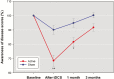
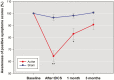
Results: Fronto-temporal transcranial direct current stimulation failed to cause significant changes in the severity of auditory verbal hallucinations and other schizophrenia symptoms. The levels of insight into illness (effect size=0.511, P<.001) and positive symptoms (effect size=0.781, P<.001) were largely promoted by 5 days of transcranial direct current stimulation relative to sham treatment. The beneficial effects on the 2 insight dimensions remained 1 month after transcranial direct current stimulation.
Conclusions: Fronto-temporal transcranial direct current stimulation is not more effective for auditory verbal hallucinations and other schizophrenia symptoms than sham treatment. But the results of transcranial direct current stimulation-associated improvement in awareness of illness and positive symptoms show promise and provide a new direction for future research into insight promotion interventions in schizophrenia.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal SM, Bose A, Shivakumar V, Narayanaswamy JC, Chhabra H, Kalmady SV, Varambally S, Nitsche MA, Venkatasubramanian G, Gangadhar BN(2016)Impact of antipsychotic medication on transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) effects in schizophrenia patients. Psychiatry Res 235:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Amador XF, Strauss DH, Yale SA, Flaum MM, Endicott J, Gorman JM(1993)Assessment of insight in psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 150:873–879. - PubMed
-
- Bergé D, Carmona S, Rovira M, Bulbena A, Salgado P, Vilarroya O(2011)Gray matter volume deficits and correlation with insight and negative symptoms in first-psychotic-episode subjects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 123:431–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

