Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Beclin-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 30107804
- PMCID: PMC6092876
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-018-1465-8
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Beclin-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The abnormal expression of Beclin-1 has recently been investigated in a variety of tumors. However, previous studies have obtained contradicting results regarding the clinical and prognostic value of Beclin-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We performed a meta-analysis to clarify the prognostic value of Beclin-1 and its correlations with clinical pathological parameters in HCC.
Methods: Relevant studies were systematically retrieved from PubMed, EMBASE, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wan Fang and Chinese VIP databases. We used the Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) to estimate the quality of the involved studies.
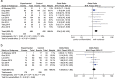
Results: Ten eligible studies with 1086 HCC patients were included in this study. Our results showed that decreased Beclin-1 expression in HCC related to histological grade [poor-undifferentiated vs. well-moderate: odds ratio (OR) = 2.34, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.65-3.32, P < 0.00001]. The pooled hazard ratio (HR) (HR = 1.43, 95% CI = 1.17-1.75, P = 0.0004) indicated that decreased Beclin-1 expression correlated with poor overall survival (OS).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis indicated that decreased Beclin-1 expression might relate to poor differentiation and unfavorable outcome in HCC.
Keywords: Beclin-1; Clinicopathological factors; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Meta-analysis; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

