Biochemical and Epigenetic Insights into L-2-Hydroxyglutarate, a Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Cancer
- PMID: 30108105
- PMCID: PMC6295227
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1727
Biochemical and Epigenetic Insights into L-2-Hydroxyglutarate, a Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Elevation of L-2-hydroxylgutarate (L-2-HG) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is due in part to reduced expression of L-2-HG dehydrogenase (L2HGDH). However, the contribution of L-2-HG to renal carcinogenesis and insight into the biochemistry and targets of this small molecule remains to be elucidated.
Experimental design: Genetic and pharmacologic approaches to modulate L-2-HG levels were assessed for effects on in vitro and in vivo phenotypes. Metabolomics was used to dissect the biochemical mechanisms that promote L-2-HG accumulation in RCC cells. Transcriptomic analysis was utilized to identify relevant targets of L-2-HG. Finally, bioinformatic and metabolomic analyses were used to assess the L-2-HG/L2HGDH axis as a function of patient outcome and cancer progression.
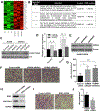
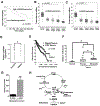
Results: L2HGDH suppresses both in vitro cell migration and in vivo tumor growth and these effects are mediated by L2HGDH's catalytic activity. Biochemical studies indicate that glutamine is the predominant carbon source for L-2-HG via the activity of malate dehydrogenase 2 (MDH2). Inhibition of the glutamine-MDH2 axis suppresses in vitro phenotypes in an L-2-HG-dependent manner. Moreover, in vivo growth of RCC cells with basal elevation of L-2-HG is suppressed by glutaminase inhibition. Transcriptomic and functional analyses demonstrate that the histone demethylase KDM6A is a target of L-2-HG in RCC. Finally, increased L-2-HG levels, L2HGDH copy loss, and lower L2HGDH expression are associated with tumor progression and/or worsened prognosis in patients with RCC.
Conclusions: Collectively, our studies provide biochemical and mechanistic insight into the biology of this small molecule and provide new opportunities for treating L-2-HG-driven kidney cancers.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: E. Emberley, A. Pan, J. Cheng, and T. Huang are employees of Calithera Biosciences. All other authors have declared no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
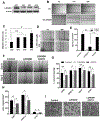
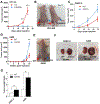
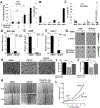
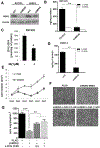
Comment in
-
Oncometabolite mechanism unravelled.Nat Rev Urol. 2018 Nov;15(11):656-657. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0086-x. Nat Rev Urol. 2018. PMID: 30185913 No abstract available.
-
Translating L-2-HG to kidney cancer at the bench and bedside.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Dec;6(Suppl 2):S103. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.11.41. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30740424 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Editorial on "Biochemical and Epigenetic Insights into L-2-Hydroxyglutarate, a Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Cancer".Ann Transl Med. 2018 Dec;6(Suppl 2):S105. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.11.43. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30740426 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Amary MF, Bacsi K, Maggiani F, Damato S, Halai D, Berisha F, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are frequent events in central chondrosarcoma and central and periosteal chondromas but not in other mesenchymal tumours. The Journal of pathology 2011;224:334–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

