Cholecystokinin Switches the Plasticity of GABA Synapses in the Dorsomedial Hypothalamus via Astrocytic ATP Release
- PMID: 30108130
- PMCID: PMC6596220
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0569-18.2018
Cholecystokinin Switches the Plasticity of GABA Synapses in the Dorsomedial Hypothalamus via Astrocytic ATP Release
Abstract
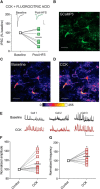
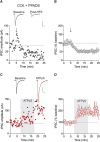
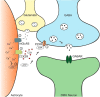
Whether synapses in appetite-regulatory brain regions undergo long-term changes in strength in response to satiety peptides is poorly understood. Here we show that following bursts of afferent activity, the neuromodulator and satiety peptide cholecystokinin (CCK) shifts the plasticity of GABA synapses in the dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus of male Sprague Dawley rats from long-term depression to long-term potentiation (LTP). This LTP requires the activation of both type 2 CCK receptors and group 5 metabotropic glutamate receptors, resulting in a rise in astrocytic intracellular calcium and subsequent ATP release. ATP then acts on presynaptic P2X receptors to trigger a prolonged increase in GABA release. Our observations demonstrate a novel form of CCK-mediated plasticity that requires astrocytic ATP release, and could serve as a mechanism for appetite regulation.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Satiety peptides, like cholecystokinin, play an important role in the central regulation of appetite, but their effect on synaptic plasticity is not well understood. The current data provide novel evidence that cholecystokinin shifts the plasticity from long-term depression to long-term potentiation at GABA synapses in the rat dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. We also demonstrate that this plasticity requires the concerted action of cholecystokinin and glutamate on astrocytes, triggering the release of the gliotransmitter ATP, which subsequently increases GABA release from neighboring inhibitory terminals. This research reveals a novel neuropeptide-induced switch in the direction of synaptic plasticity that requires astrocytes, and could represent a new mechanism by which cholecystokinin regulates appetite.
Keywords: ATP; GABA; appetite; astrocytes; cholecystokinin; dorsomedial hypothalamus.
Copyright © 2018 the authors 0270-6474/18/388515-11$15.00/0.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Postsynaptic Depolarization Enhances GABA Drive to Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Neurons through Somatodendritic Cholecystokinin Release.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 23;35(38):13160-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3123-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26400945 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic origin of CB1-dependent tonic inhibition of GABA release at cholecystokinin-positive basket cell to pyramidal cell synapses in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 1;578(Pt 1):233-47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.115691. Epub 2006 Oct 19. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17053036 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-mediated distributed plasticity at hypothalamic glutamate synapses.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):391-403. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.021. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19914187 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Central Synapses by Astrocyte-Released ATP and Postsynaptic P2X Receptors.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:9454275. doi: 10.1155/2017/9454275. Epub 2017 Aug 6. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28845311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2X receptors and synaptic plasticity.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):137-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.076. Epub 2008 Apr 23. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18495357 Review.
Cited by
-
Purinergic P2 and glutamate NMDA receptor coupling contributes to osmotically driven excitability in hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory neurons.J Physiol. 2021 Jul;599(14):3531-3547. doi: 10.1113/JP281411. Epub 2021 Jun 26. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34053068 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved neuropeptide system links head and body motor circuits to enable adaptive behavior.Elife. 2021 Nov 12;10:e71747. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71747. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34766905 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic Cells in the Brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 10;16:892497. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.892497. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35755777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatodendritic Release of Cholecystokinin Potentiates GABAergic Synapses Onto Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Cells.Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Jan 15;93(2):197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.06.011. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 35961792 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic plasticity and the role of astrocytes in central metabolic circuits.WIREs Mech Dis. 2024 Jan-Feb;16(1):e1632. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1632. Epub 2023 Oct 13. WIREs Mech Dis. 2024. PMID: 37833830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
