Gingerol suppresses sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by modulating methylsulfonylmethane and dimethylamine production
- PMID: 30108263
- PMCID: PMC6092401
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30522-6
Gingerol suppresses sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by modulating methylsulfonylmethane and dimethylamine production
Abstract
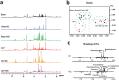
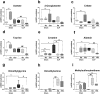
Acute kidney injury (AKI) and metabolic dysfunction are critical complications in sepsis syndrome; however, their pathophysiological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Therefore, we evaluated whether the pharmacological properties of 6-gingerol (6G) and 10-gingerol (10G) could modulate AKI and metabolic disruption in a rat model of sepsis (faecal peritonitis). Animals from the sham and AKI groups were intraperitoneally injected with 6G or 10G (25 mg/kg). Septic AKI decreased creatinine clearance and renal antioxidant activity, but enhanced oxidative stress and the renal mRNA levels of tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and transforming growth factor-β. Both phenol compounds repaired kidney function through antioxidant activity related to decreased oxidative/nitrosative stress and proinflammatory cytokines. Metabolomics analysis indicated different metabolic profiles for the sham surgery group, caecal ligation and puncture model alone group, and sepsis groups treated with gingerols. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance analysis detected important increases in urinary creatine, allantoin, and dimethylglycine levels in septic rats. However, dimethylamine and methylsulfonylmethane metabolites were more frequently detected in septic animals treated with 6G or 10G, and were associated with increased survival of septic animals. Gingerols attenuated septic AKI by decreasing renal disturbances, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response through a mechanism possibly correlated with increased production of dimethylamine and methylsulfonylmethane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

