Integrative metagenomic and biochemical studies on rifamycin ADP-ribosyltransferases discovered in the sediment microbiome
- PMID: 30108275
- PMCID: PMC6092378
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30547-x
Integrative metagenomic and biochemical studies on rifamycin ADP-ribosyltransferases discovered in the sediment microbiome
Abstract
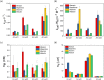
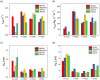
Antibiotic resistance is a serious and growing threat to human health. The environmental microbiome is a rich reservoir of resistomes, offering opportunities to discover new antibiotic resistance genes. Here we demonstrate an integrative approach of utilizing gene sequence and protein structural information to characterize unidentified genes that are responsible for the resistance to the action of rifamycin antibiotic rifampin, a first-line antimicrobial agent to treat tuberculosis. Biochemical characterization of four environmental metagenomic proteins indicates that they are adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribosyltransferases and effective in the development of resistance to FDA-approved rifamycins. Our analysis suggests that even a single residue with low sequence conservation plays an important role in regulating the degrees of antibiotic resistance. In addition to advancing our understanding of antibiotic resistomes, this work demonstrates the importance of an integrative approach to discover new metagenomic genes and decipher their biochemical functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rifamycin antibiotic resistance by ADP-ribosylation: Structure and diversity of Arr.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 25;105(12):4886-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711939105. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18349144 Free PMC article.
-
Arr-cb Is a Rifampin Resistance Determinant Found Active or Cryptic in Clostridium bolteae Strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jul 25;61(8):e00301-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00301-17. Print 2017 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28533241 Free PMC article.
-
Abundance and Diversity of Phages, Microbial Taxa, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Sediments of the River Ganges Through Metagenomic Approach.Microb Drug Resist. 2021 Oct;27(10):1336-1354. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0431. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Microb Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 33913739
-
The Enzymes of the Rifamycin Antibiotic Resistome.Acc Chem Res. 2021 May 4;54(9):2065-2075. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00048. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33877820 Review.
-
Using metagenomics to investigate human and environmental resistomes.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Oct 1;72(10):2690-2703. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx199. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28673041 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery and Characterization of Polymyxin-Resistance Genes pmrE and pmrF from Sediment and Seawater Microbiome.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0273622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02736-22. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36602384 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-ribosylation systems in bacteria and viruses.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Apr 17;19:2366-2383. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.023. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rifamycin antibiotics and the mechanisms of their failure.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021 Nov;74(11):786-798. doi: 10.1038/s41429-021-00462-x. Epub 2021 Aug 16. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 34400805 Review.
-
Genomic epidemiology of rifampicin ADP-ribosyltransferase (Arr) in the Bacteria domain.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 5;11(1):19775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99255-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34611248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marriner, G. A. et al. In Third World Diseases Vol. 7 (ed. Elliott, R. L.) 47–124 (Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2011).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

