Whole exome sequencing study identifies novel rare and common Alzheimer's-Associated variants involved in immune response and transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 30108311
- PMCID: PMC6375806
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-018-0112-7
Whole exome sequencing study identifies novel rare and common Alzheimer's-Associated variants involved in immune response and transcriptional regulation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Whole exome sequencing study identifies novel rare and common Alzheimer's-Associated variants involved in immune response and transcriptional regulation.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Aug;25(8):1901-1903. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0529-7. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31636380 Free PMC article.
Abstract
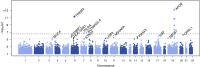
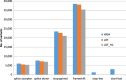
The Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project (ADSP) undertook whole exome sequencing in 5,740 late-onset Alzheimer disease (AD) cases and 5,096 cognitively normal controls primarily of European ancestry (EA), among whom 218 cases and 177 controls were Caribbean Hispanic (CH). An age-, sex- and APOE based risk score and family history were used to select cases most likely to harbor novel AD risk variants and controls least likely to develop AD by age 85 years. We tested ~1.5 million single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and 50,000 insertion-deletion polymorphisms (indels) for association to AD, using multiple models considering individual variants as well as gene-based tests aggregating rare, predicted functional, and loss of function variants. Sixteen single variants and 19 genes that met criteria for significant or suggestive associations after multiple-testing correction were evaluated for replication in four independent samples; three with whole exome sequencing (2,778 cases, 7,262 controls) and one with genome-wide genotyping imputed to the Haplotype Reference Consortium panel (9,343 cases, 11,527 controls). The top findings in the discovery sample were also followed-up in the ADSP whole-genome sequenced family-based dataset (197 members of 42 EA families and 501 members of 157 CH families). We identified novel and predicted functional genetic variants in genes previously associated with AD. We also detected associations in three novel genes: IGHG3 (p = 9.8 × 10-7), an immunoglobulin gene whose antibodies interact with β-amyloid, a long non-coding RNA AC099552.4 (p = 1.2 × 10-7), and a zinc-finger protein ZNF655 (gene-based p = 5.0 × 10-6). The latter two suggest an important role for transcriptional regulation in AD pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Celine Bellenguez received personal fees from Genoscrenn unrelated to current study. HS reports grants from Austrian Science Fond (FWF) and Österreichische Nationalbank Anniversary Fund during the conduct of the study. AMG received grants from NIA, Genentech, Pfizer, and Astra Zeneca as well as personal fees from Finnegan HC, Cognition Therapeutics, Dickstein Shapiro, Genentech, and Amgen, all unrelated to the current study. In addition, AMG has a patent (US20070258898) issued, and a patent with royalties paid by Taconic. J-FD received grants and personal fees from IPSEN and Novartis, and personal fees from Newron. MAP-V received personal fees from Athena Neurosciences unrelated to current study. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058635/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054060/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG052427/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG054936/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052411/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG053303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG066107/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I 904/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG047133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG041689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058589/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052410/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM012535/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

