Unbiased shRNA screening, using a combination of FACS and high-throughput sequencing, enables identification of novel modifiers of Polycomb silencing
- PMID: 30108332
- PMCID: PMC6092423
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30649-6
Unbiased shRNA screening, using a combination of FACS and high-throughput sequencing, enables identification of novel modifiers of Polycomb silencing
Abstract
Polycomb silencing is an important and rapidly growing field that is relevant to a broad range of aspects of human health, including cancer and stem cell biology. To date, the regulatory mechanisms for the fine-tuning of Polycomb silencing remain unclear, but it is likely that there is a series of unidentified factors that functionally modify or balance the silencing. However, a practical gene screening strategy for identifying such factors has not yet been developed. The failure of screening strategies used thus far is probably due to the effect of the loss-of-function phenotypes of these factors on cell cycle progression. Here, by applying fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) and high-throughput sequencing (HTS) technology in a large-scale lentivirus-mediated shRNA screening, we obtained a consecutive dataset from all shRNAs tested, which highlighted a substantial number of genes that may control Polycomb silencing. We consider that this unbiased strategy can readily be applied to a wide range of studies to uncover novel regulatory layers for expression of genes of interest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


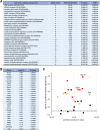
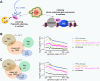
Similar articles
-
Establishing an Infrastructure for High-Throughput Short-Interfering RNA Screening.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1470:1-13. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6337-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27581280
-
A genome-wide shRNA screen for new OxPhos related genes.Mitochondrion. 2011 May;11(3):467-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2011.01.007. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Mitochondrion. 2011. PMID: 21292037
-
Short-term cytotoxic effects and long-term instability of RNAi delivered using lentiviral vectors.BMC Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 3;5:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-9. BMC Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15291968 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh-throughput FACS-based screening for directed enzyme evolution.Chembiochem. 2009 Nov 23;10(17):2704-15. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200900384. Chembiochem. 2009. PMID: 19780076 Review.
-
Fluorescent genetic barcoding for cellular multiplex analyses.Exp Hematol. 2018 Nov;67:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Exp Hematol. 2018. PMID: 30098396 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hox transcription factor Ubx stabilizes lineage commitment by suppressing cellular plasticity in Drosophila.Elife. 2019 May 3;8:e42675. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42675. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31050646 Free PMC article.
-
The deletion of the protein phosphatase 1 regulator NIPP1 in testis causes hyperphosphorylation and degradation of the histone methyltransferase EZH2.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 23;293(47):18031-18039. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC118.005577. Epub 2018 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30305391 Free PMC article.
-
The ACF chromatin-remodeling complex is essential for Polycomb repression.Elife. 2022 Mar 8;11:e77595. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77595. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35257662 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

