MiR-96 enhances cellular proliferation and tumorigenicity of human cervical carcinoma cells through PTPN9
- PMID: 30108433
- PMCID: PMC6087804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.10.020
MiR-96 enhances cellular proliferation and tumorigenicity of human cervical carcinoma cells through PTPN9
Abstract
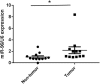
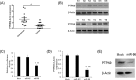
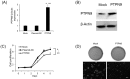
Up to date, the cervical cancer remains to be one of the leading gynecological malignancies worldwide. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles in the process of tumor initiation and progression. However, miR-96 has rarely been investigated in human cervical carcinoma. We aimed to investigate the biological function and underlying molecular mechanism of miR-96 in human cervical carcinoma. MiR-96 levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 9 (PTPN9) mRNA and protein levels were investigated by qRT-PCR and western blotting. The cellular proliferation in cervical cells was monitored by CyQuant assay. Soft agar assay was employed to determine the tumorigenicity. 3' UTR luciferase assay was used to validate the target gene of miR-96. SPSS was used to analyze statistical significance in different treatment. MiR-96 was dramatically upregulated in human cervical tumor tissues. Overexpression of miR-96 was found to significantly promote the cellular proliferation and tumorigenicity of cervical cells. Furthermore, we showed that PTPN9 was a direct target gene of miR-96 and had opposite effect to those of miR-96 on cervical cells. MiR-96 may promote the cellular proliferation and tumorigenicity of cervical cells by silencing PTPN9. Our study highlights an importantly regulatory role of miR-96 and suggests that an appropriate manipulation of miR-96 may be a new treatment of human cervical carcinoma in the future.
Keywords: Cervical carcinoma; MiR-96; PTPN9; Proliferation.
Figures

References
-
- Agirre X., Jimenez-Velasco A., San Jose-Eneriz E. Down-regulation of hsamiR- 10a in chronic myeloid leukemia CD34+ cells increases USF2-mediated cell growth. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008;6:1830–1840. - PubMed
-
- Calin G.A., Croce C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Carroll A.P., Goodall G.J., Liu B. Understanding principles of miRNA target recognition and function through integrated biological and bioinformatics approaches. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2014;5:361–379. - PubMed
-
- Du W.W., Fang L., Li M. MicroRNA miR-24 enhances tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting PTPN9 and PTPRF to promote EGF signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2013;126:1440–1453. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

