Functional mechanism of Ginsenosides on tumor growth and metastasis
- PMID: 30108441
- PMCID: PMC6087812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.01.012
Functional mechanism of Ginsenosides on tumor growth and metastasis
Abstract
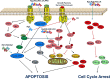
Ginsengs, has long been used as one medicinal herb in China for more than two thousand years. Many studies have shown that ginsengs have preventive and therapeutic roles for cancer, and play a good complementary role in cancer treatment. Ginsenosides, as most important constituents of ginseng, have been extensively investigated and emphasized in cancer chemoprevention and therapeutics. However, the functional mechanism of Ginsenosides on cancer is not well known. This review will focus on introducing the functional mechanisms of ginsenosides and their metabolites, which regulate signaling pathways related with tumor growth and metastasis. Ginsenosides inhibit tumor growth via upregulating tumor apoptosis, inducing tumor cell differentiation and targeting cancer stem cells. In addition, Ginsenosides regulate tumor microenvironment via suppressing tumor angiogenesis-related proteins and pathways. Structural modification of ginsenosides and their administration alone or combinations with other Chinese medicines or chemical medicines have recently been developed to be a new therapeutic strategy for cancer.
Keywords: Functional mechanism; Ginsenosides; Tumor growth; Tumor metastasis.
Figures

References
-
- Azike C.G., Charpentier P.A., Lui E.M. Stimulation and suppression of innate immune function by American ginseng polysaccharides: biological relevance and identification of bioactives. Pharm. Res. 2015;32:876–897. - PubMed
-
- Bae E.A., Choo M.K., Park E.K., Park S.Y., Shin H.Y., Kim D.H. Metabolism of ginsenoside R(c) by human intestinal bacteria and its related antiallergic activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002;25:743. - PubMed
-
- Bae E.A., Shin J.E., Kim D.H. Metabolism of ginsenoside Re by human intestinal microflora and its estrogenic effect. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005;28:1903. - PubMed
-
- Brown D.M., Donaldson K., Borm P.J., Schins R.P., Dehnhardt M., Gilmour P., Jimenez L.A., Stone V. Calcium and ROS-mediated activation of transcription factors and TNF-alpha cytokine gene expression in macrophages exposed to ultrafine particles. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004;286:L344. - PubMed
-
- Chae S., Piao M.J., Kang K.A., Zhang R., Kim K.C., Youn U.J., Nam K.W., Lee J.H., Hyun J.W. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-1 induced by oxidative stress in human keratinocytes by mangiferin isolated from Anemarrhena asphodeloides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011;75:2321–2325. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

