Association of stressful life events and psychological problems profile: Results from a large-scale cross-sectional study among Iranian industrial employees using Bayesian quantile structural equation model
- PMID: 30108466
- PMCID: PMC6088219
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2018-1051
Association of stressful life events and psychological problems profile: Results from a large-scale cross-sectional study among Iranian industrial employees using Bayesian quantile structural equation model
Abstract
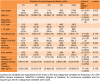
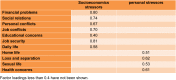
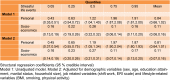
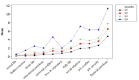
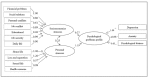
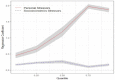
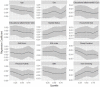
Objectives: The current study aimed at evaluating the major domains of stressful life events and their association with psychological problems profile in a large sample of Iranian industrial manufacturing employees. Methods: In a cross-sectional study, 3,063 participants were randomly selected from 16,000 employees working in a big industrial company in Isfahan, Iran. Three common psychological problems i.e. depression, anxiety and psychological distress were evaluated using Persian validated version of Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and 12-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12), respectively. Self-perceived frequency and intensity of stressful life events were measured by stressful life event (SLE) questionnaire. Bayesian quantile structural equation model in R free statistical software (version 3.4) was used for evaluating the association of stressful life events and levels of psychological problems profile. Results: Using factor analysis, two major domains i.e. socioeconomic and personal stressors were derived from 11 life stressors and a unified measure i.e. psychological problem profile was extracted from three common psychological problems. Financial and daily life stressors had the highest and sexual problems showed lowest intensity. Quantile structural equation model revealed that the psychological problems profile scores had stronger association with personal (β: ranging from 0.45, 1.87) than socioeconomics stressors (β: ranging from 0.11, 0.27). The association of socioeconomic stressors was fairly uniform across quantiles of psychological problems scores, while personal stressors showed stronger association in higher quantiles, meaning that employees with higher mental health problems more experienced personal stressors. Conclusions: Life stressors particularly personal showed direct association with intensity of psychological problems in manufacturing employees. Life stressors are more perceived by employees with higher intensity of psychological problems. The results of current study can be useful in planning occupational health programs in order to improve psychological health and job productivity.
Keywords: industrial employees; psychological problems; quantile structural equation model; stressful life events.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DM-5®) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Pub; 2013.
-
- Andrea H, Bultmann U, Beurskens AJ, Swaen GM, van Schayck CP, Kant IJ. Anxiety and depression in the working population using the had scale - psychometrics, prevalence and relationships with psychosocial work characteristics. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2004;39:637–646. - PubMed
-
- Bonde JP. Psychosocial factors at work and risk of depression: A systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. Occup Environ Med. 2008;65:438–445. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
