Subjective Vividness of Kinesthetic Motor Imagery Is Associated With the Similarity in Magnitude of Sensorimotor Event-Related Desynchronization Between Motor Execution and Motor Imagery
- PMID: 30108492
- PMCID: PMC6079198
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00295
Subjective Vividness of Kinesthetic Motor Imagery Is Associated With the Similarity in Magnitude of Sensorimotor Event-Related Desynchronization Between Motor Execution and Motor Imagery
Abstract
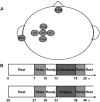
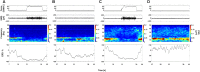
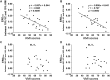
In the field of psychology, it has been well established that there are two types of motor imagery such as kinesthetic motor imagery (KMI) and visual motor imagery (VMI), and the subjective evaluation for vividness of motor imagery each differs across individuals. This study aimed to examine how the motor imagery ability assessed by the psychological scores is associated with the physiological measure using electroencephalogram (EEG) sensorimotor rhythm during KMI task. First, 20 healthy young individuals evaluated subjectively how vividly they can perform each of KMI and VMI by using the Kinesthetic and Visual Imagery Questionnaire (KVIQ). We assessed their motor imagery abilities by summing each of KMI and VMI scores in KVIQ (KMItotal and VMItotal). Second, in physiological experiments, they repeated two strengths (10 and 40% of maximal effort) of isometric voluntary wrist-dorsiflexion. Right after each contraction, they also performed its KMI. The scalp EEGs over the sensorimotor cortex were recorded during the tasks. The EEG power is known to decrease in the alpha-and-beta band (7-35 Hz) from resting state to performing state of voluntary contraction (VC) or motor imagery. This phenomenon is referred to as event-related desynchronization (ERD). For each strength of the tasks, we calculated the maximal peak of ERD during VC, and that during its KMI, and measured the degree of similarity (ERDsim) between them. The results showed significant negative correlations between KMItotal and ERDsim for both strengths (p < 0.05) (i.e., the higher the KMItotal, the smaller the ERDsim). These findings suggest that in healthy individuals with higher motor imagery ability from a first-person perspective, KMI efficiently engages the shared cortical circuits corresponding with motor execution, including the sensorimotor cortex, with high compliance.
Keywords: corticospinal excitability; electroencephalogram; motor imagery; sensorimotor rhythm; the Kinesthetic and Visual Imagery Questionnaire.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of kinesthetic motor imagery compared with visual motor imageries.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 12;11(1):3751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82241-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33580093 Free PMC article.
-
Gymnasts' Ability to Modulate Sensorimotor Rhythms During Kinesthetic Motor Imagery of Sports Non-specific Movements Superior to Non-gymnasts.Front Sports Act Living. 2021 Nov 4;3:757308. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2021.757308. eCollection 2021. Front Sports Act Living. 2021. PMID: 34805979 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Kinesthetic/Visual Motor Imagery Difficulty and Event-Related Desynchronization/Synchronization.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:1911-1914. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512673. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30440771
-
ERD/ERS patterns reflecting sensorimotor activation and deactivation.Prog Brain Res. 2006;159:211-22. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)59014-4. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17071233 Review.
-
How Kinesthetic Motor Imagery works: a predictive-processing theory of visualization in sports and motor expertise.J Physiol Paris. 2015 Feb-Jun;109(1-3):53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Mar 25. J Physiol Paris. 2015. PMID: 25817985 Review.
Cited by
-
Vibration-Induced Illusory Movement Task Can Induce Functional Recovery in Patients With Subacute Stroke.Cureus. 2024 Aug 12;16(8):e66667. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66667. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39262538 Free PMC article.
-
The format of mental imagery: from a critical review to an integrated embodied representation approach.Cogn Process. 2019 Aug;20(3):277-289. doi: 10.1007/s10339-019-00908-z. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Cogn Process. 2019. PMID: 30798484 Review.
-
Characterization of kinesthetic motor imagery compared with visual motor imageries.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 12;11(1):3751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82241-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33580093 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Tactile Imagery Training on Reaction Time in Healthy Participants.Brain Sci. 2023 Feb 14;13(2):321. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020321. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36831864 Free PMC article.
-
Gymnasts' Ability to Modulate Sensorimotor Rhythms During Kinesthetic Motor Imagery of Sports Non-specific Movements Superior to Non-gymnasts.Front Sports Act Living. 2021 Nov 4;3:757308. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2021.757308. eCollection 2021. Front Sports Act Living. 2021. PMID: 34805979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aftanas L. I., Varlamov A. A., Pavlov S. V., Makhnev V. P., Reva N. V. (2002). Time-dependent cortical asymmetries induced by emotional arousal: EEG analysis of event-related synchronization and desynchronization in individually defined frequency bands. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 44 67–82. 10.1016/S0167-8760(01)00194-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ang K. K., Guan C., Phua K. S., Wang C., Zhou L., Tang K. Y., et al. (2014). Brain-computer interface-based robotic end effector system for wrist and hand rehabilitation: results of a three-armed randomized controlled trial for chronic stroke. Front. Neuroeng. 7:30. 10.3389/fneng.2014.00030 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

