Effects of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition on Cardiovascular Risk of Adult Endotoxemic Female Rats: Role of Estrogen
- PMID: 30108513
- PMCID: PMC6079304
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01020
Effects of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition on Cardiovascular Risk of Adult Endotoxemic Female Rats: Role of Estrogen
Abstract
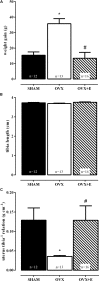
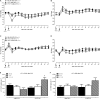
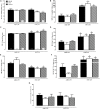
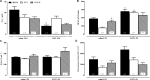
Aim: Autonomic modulation responds to ovarian hormones and estrogen increases nitric oxide bioavailability. Also, females have minor susceptibility to sepsis and a higher survival rate. However, few studies have evaluated the role of estrogen in cardiovascular, autonomic, and oxidative parameters during initial endotoxemia and under inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) inhibition in female rats. Methods: Female wistar rats were subjected to ovariectomy and divided into three groups: OVX (ovariectomized), OVX+E (OVX plus daily estradiol) and SHAM (false surgery). After 8 weeks, mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were recorded in non-anesthetized catheterized rats, before and after intravenous LPS injection, preceded by S-methylisothiourea sulfate (SMT) injection, or sterile saline. Cardiovascular recordings underwent spectral analysis for evaluation of autonomic modulation. Two hours after LPS, plasma was collected to assess total radical-trapping antioxidant (TRAP), nitrite levels (NO2), lipoperoxidation (LOOH), and paraoxonase 1 (PON1) activity. Results: Two hours after LPS, females treated with SMT presented a decrease of MAP, when compared to saline-LPS groups. At this same time, all SMT+LPS groups presented an increase of sympathetic and a decrease of parasympathetic modulation of HR. Two hours after saline+LPS, OVX presented decreased total radical-trapping antioxidant (TRAP) compared to SHAM. When treated with SMT+LPS, OVX did not altered TRAP, while estradiol reduced LOOH levels. Conclusion: iNOS would be responsible for sympathetic inhibition and consumption of antioxidant reserves of females during endotoxemia, since iNOS is inhibited, treatment with estradiol could be protective in inflammatory challenges.
Keywords: blood pressure; endotoxemia; heart rate; lipopolysaccharide; nitric oxide; ovariectomy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular risk and the effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition in female rats: The role of estrogen.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Oct 15;97:38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.07.016. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 28757113
-
Role of the iNOS isoform in the cardiovascular dysfunctions of male rats with 6-OHDA-induced Parkinsonism.Nitric Oxide. 2023 May 1;134-135:49-60. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2023.04.003. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Nitric Oxide. 2023. PMID: 37054808
-
Influence of propofol on blood pressure spectrum in sepsis and the role of inducible nitric oxide synthase.Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2009 Jun;47(2):62-70. doi: 10.1016/S1875-4597(09)60026-6. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2009. PMID: 19527966
-
Metalloendopeptidase inhibition regulates phosphorylation of p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase and nitric oxide synthase in heart after endotoxemia.Shock. 2003 Oct;20(4):375-81. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000087202.34916.0c. Shock. 2003. PMID: 14501953
-
Comparison between selective and nonselective nitric oxide synthase inhibition and phenylephrine in normal and endotoxic swine.Crit Care Med. 2000 Sep;28(9):3257-67. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200009000-00022. Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 11008990
Cited by
-
Mind the Gap: Unraveling the Intricate Dance Between Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias and Bone Health.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024 Feb;22(1):165-176. doi: 10.1007/s11914-023-00847-x. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024. PMID: 38285083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dapagliflozin Mitigates Hypotension in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Inflammation Independent of Glycemia Level.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 8;15(6):1683. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061683. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ariza D., Sisdeli L., Crestani C. C., Fazan R., Martins-Pinge M. C. (2015). Dysautonomias in Parkinson’s disease: cardiovascular changes and autonomic modulation in conscious rats after infusion of bilateral 6-OHDA in substantia nigra. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308 H250–H257. 10.1152/ajpheart.00406.2014 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

