Borderline Personality Disorder With Cocaine Dependence: Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Amygdala Functional Connectivity
- PMID: 30108525
- PMCID: PMC6079279
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00328
Borderline Personality Disorder With Cocaine Dependence: Impulsivity, Emotional Dysregulation and Amygdala Functional Connectivity
Abstract
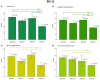
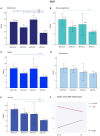
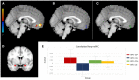
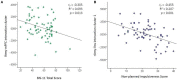
Background: Borderline personality disorder is present in 19% of cocaine dependence cases; however, this dual pathology is poorly understood. We wished to characterize the dual pathology and find its functional connectivity correlates to better understand it. Methods: We recruited 69 participants divided into 4 groups: dual pathology (n = 20), cocaine dependence without borderline personality disorder (n = 19), borderline personality without cocaine dependence (n = 10) and healthy controls (n = 20). We used self-reported instruments to measure impulsivity and emotional dysregulation. We acquired resting state fMRI and performed seed-based analyses of the functional connectivity of bilateral amygdala. Results: Borderline personality disorder and cocaine dependence as factors had opposing effects in impulsivity and emotional dysregulation, as well as on functional connectivity between left amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex. On the other hand, in the functional connectivity between right amygdala and left insula, the effect of having both disorders was instead additive, reducing functional connectivity strength. The significant functional connectivity clusters were correlated with impulsivity and emotional dysregulation. Conclusions: In this study, we found that clinical scores of dual pathology patients were closer to those of borderline personality disorder without cocaine dependence than to those of cocaine dependence without borderline personality disorder, while amygdala-medial prefrontal cortex functional connectivity patterns in dual pathology patients were closer to healthy controls than expected.
Keywords: amygdala; borderline personality disorder; cocaine dependence; dual pathology; functional connectivity; neuroimaging.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cocaine users with comorbid Cluster B personality disorders show dysfunctional brain activation and connectivity in the emotional regulation networks during negative emotion maintenance and reappraisal.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Dec;23(12):1698-707. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.04.012. Epub 2013 May 25. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23712090
-
Altered cortical thickness and emotional dysregulation in adolescents with borderline personality disorder.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2023;14(1):2163768. doi: 10.1080/20008066.2022.2163768. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2023. PMID: 37052085 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation of basolateral and central amygdala effective connectivity predicts the stability of emotion-related impulsivity in adolescents and emerging adults with borderline personality symptoms: a resting-state fMRI study.Psychol Med. 2023 Jun;53(8):3533-3547. doi: 10.1017/S0033291722000101. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Psychol Med. 2023. PMID: 35225192
-
Emotion dysregulation in borderline personality disorder: A fronto-limbic imbalance?Curr Opin Psychol. 2021 Feb;37:114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.12.002. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Curr Opin Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33422855 Review.
-
Re-evaluating our focus in addiction: emotional dysregulation is a critical driver of relapse to drug use.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 9;14(1):467. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03159-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39521844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Childhood Maltreatment on Social Cognition and Brain Functional Connectivity in Borderline Personality Disorder Patients.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Mar 29;10:156. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00156. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30988667 Free PMC article.
-
The Mexican magnetic resonance imaging dataset of patients with cocaine use disorder: SUDMEX CONN.Sci Data. 2022 Mar 31;9(1):133. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01251-3. Sci Data. 2022. PMID: 35361781 Free PMC article.
-
Recontextualizing the subject of phenomenological psychopathology: Establishing a new paradigm case.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 21;13:1035967. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1035967. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36339859 Free PMC article.
-
Amygdala Resting State Connectivity Differences between Bipolar II and Borderline Personality Disorders.Neuropsychobiology. 2019;78(4):229-237. doi: 10.1159/000502440. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Neuropsychobiology. 2019. PMID: 31553999 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion regulation in substance use disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Addiction. 2023 Jan;118(1):30-47. doi: 10.1111/add.16001. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Addiction. 2023. PMID: 35851975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Compton WM, Thomas YF, Stinson FS, Grant BF. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV drug abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry (2007) 64:566–76. 10.1001/archpsyc.64.5.566 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szerman N, Martinez-Raga J. Dual disorders: two different mental disorders? Adv Dual Diagn. (2015) 8 10.1108/ADD-03-2015-0004 - DOI
-
- Arias F, Szerman N, Vega P, Mesias B, Basurte I, Morant C, et al. Abuse or dependence on cannabis and other psychiatric disorders. Madrid study on dual pathology prevalence. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. (2013) 41:122–9. - PubMed
-
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th edn Washington, DC: Association. AP; (2000).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

