The Role of Lipoproteins in Mycoplasma-Mediated Immunomodulation
- PMID: 30108558
- PMCID: PMC6080569
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01682
The Role of Lipoproteins in Mycoplasma-Mediated Immunomodulation
Abstract
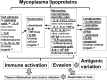
Mycoplasma infections, such as walking pneumonia or pelvic inflammatory diseases, are a major threat to public health. Despite their relatively small physical and genomic size, mycoplasmas are known to elicit strong host immune responses, generally inflammatory, while also being able to evade the immune system. The mycoplasma membrane is composed of approximately two-thirds protein and one-third lipid and contains several lipoproteins that are known to regulate host immune responses. Herein, the immunomodulatory effects of mycoplasma lipoproteins are reviewed. A better understanding of the immunomodulatory effects, both activating and evasive, of Mycoplasma surface lipoproteins will contribute to understanding mechanisms potentially relevant to mycoplasma disease vaccine development and treatment.
Keywords: immune modulation; immune system; inflammation; lipoproteins; mycoplasma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Cross-Talk between Spirochetal Lipoproteins and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2014 Jun 30;5:310. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00310. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25071771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular biology and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998 Dec;62(4):1094-156. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.62.4.1094-1156.1998. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9841667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The central role of lipoproteins in the pathogenesis of mycoplasmoses.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Nov 21;153(1-2):44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.05.031. Epub 2011 May 25. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21684094 Review.
-
[Pathogenic factors of mycoplasma].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2015;70(4):369-74. doi: 10.3412/jsb.70.369. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26632216 Review. Japanese.
-
Interactions between mycoplasma lipoproteins and the host immune system.Trends Microbiol. 1999 Dec;7(12):493-9. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(99)01641-8. Trends Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10603485 Review.
Cited by
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae lipids license TLR-4 for activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy to evoke a proinflammatory response.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Jan;203(1):66-79. doi: 10.1111/cei.13510. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32894580 Free PMC article.
-
Host cell interactions of novel antigenic membrane proteins of Mycoplasma agalactiae.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Apr 8;22(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02512-2. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35395771 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of the Slow Growth of Mycoplasma hominis on Different Energy Sources.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 7;12:918557. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.918557. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35873139 Free PMC article.
-
In silico structural homology modeling and functional characterization of Mycoplasma gallisepticum variable lipoprotein hemagglutin proteins.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Aug 4;9:943831. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.943831. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35990271 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoproteins Are Potent Activators of Nuclear Factor Kappa B in Mammary Epithelial Cells and Virulence Factors in Mycoplasma bovis Mastitis.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 8;10(11):2209. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10112209. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36363800 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

