Design and synthesis of novel selective estrogen receptor degradation inducers based on the diphenylheptane skeleton
- PMID: 30108709
- PMCID: PMC6072319
- DOI: 10.1039/c6md00553e
Design and synthesis of novel selective estrogen receptor degradation inducers based on the diphenylheptane skeleton
Abstract
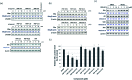
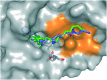
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a family of nuclear receptors (NRs) that regulate physiological effects such as reproduction and bone homeostasis. It has been reported that approximately 70% of human breast cancers are hormone-dependent and ERα-positive. Recently, novel anti-breast cancer drugs based on different mechanisms of action have received significant attention. In this article, we have designed and synthesized a selective ER degradation inducer based on the diphenylheptane skeleton. Western blotting analysis revealed that PBP-NC10 degraded ERα through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. We also performed computational docking analysis to predict the binding mode of PBP-NC10 to ERα.
Figures





References
-
- Hall J. M., McDonnell D. P. Mol. Interventions. 2005;5:343. - PubMed
-
- Walter P., Green S., Greene G., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Jeltsch J. M., Staub A., Jensen E., Scrase G., Waterfield M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1985;82:7889. - PMC - PubMed
- Holst F., Stahl P. R., Ruiz C., Hellwinkel O., Jehan Z., Wendland M., Lebeau A., Terracciano L., Al-Kuraya K., Jänicke F., Sauter G., Simon R. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:655. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

