Identification of a potent kinase inhibitor targeting EML4-ALK fusion protein in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 30108712
- PMCID: PMC6071718
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00305f
Identification of a potent kinase inhibitor targeting EML4-ALK fusion protein in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
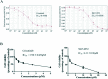
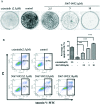
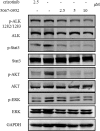
ALK-fusion proteins play a fundamental role in the development of about 5% of non-small cell lung cancers. Herein, we identified the compound 5067-0952 as a potent ALK inhibitor, which inhibited cell growth, induced apoptosis, and suppressed the phosphorylation of ALK, subsequently blocking its downstream signaling pathway.
Figures
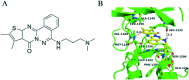
Similar articles
-
Monomerization of ALK Fusion Proteins as a Therapeutic Strategy in ALK-Rearranged Non-small Cell Lung Cancers.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 2;10:419. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00419. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32300555 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors in the treatment of ALK-driven lung cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Mar;117:343-356. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Jan 8. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28077299 Review.
-
A new human lung adenocarcinoma cell line harboring the EML4-ALK fusion gene.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014 Oct;44(10):963-8. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyu110. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25170107
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK): structure, oncogenic activation, and pharmacological inhibition.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Feb;68(1):68-94. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23201355 Review.
-
Activation of HER family signaling as a mechanism of acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Nov 15;18(22):6219-26. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0392. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22843788
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Jemal A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L., Alexander R. E., Maclennan G. T., Cummings O. W., Montironi R., Lopez-Beltran A., Cramer H. M., Davidson D. D., Zhang S. Mod. Pathol. 2012;25:347–369. - PubMed
-
- Soda M., Choi Y. L., Enomoto M., Takada S., Yamashita Y., Ishikawa S., Fujiwara S., Watanabe H., Kurashina K., Hatanaka H., Bando M., Ohno S., Ishikawa Y., Aburatani H., Niki T., Sohara Y., Sugiyama Y., Mano H. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi K., Soda M., Togashi Y., Suzuki R., Sakata S., Hatano S., Asaka R., Hamanaka W., Ninomiya H., Uehara H., Lim Choi Y., Satoh Y., Okumura S., Nakagawa K., Mano H., Ishikawa Y. Nat. Med. 2012;18:378–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

