Identification of a potent kinase inhibitor targeting EML4-ALK fusion protein in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 30108712
- PMCID: PMC6071718
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00305f
Identification of a potent kinase inhibitor targeting EML4-ALK fusion protein in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
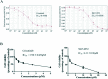
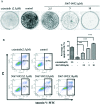
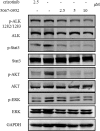
ALK-fusion proteins play a fundamental role in the development of about 5% of non-small cell lung cancers. Herein, we identified the compound 5067-0952 as a potent ALK inhibitor, which inhibited cell growth, induced apoptosis, and suppressed the phosphorylation of ALK, subsequently blocking its downstream signaling pathway.
Figures
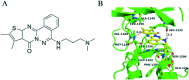
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Jemal A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L., Alexander R. E., Maclennan G. T., Cummings O. W., Montironi R., Lopez-Beltran A., Cramer H. M., Davidson D. D., Zhang S. Mod. Pathol. 2012;25:347–369. - PubMed
-
- Soda M., Choi Y. L., Enomoto M., Takada S., Yamashita Y., Ishikawa S., Fujiwara S., Watanabe H., Kurashina K., Hatanaka H., Bando M., Ohno S., Ishikawa Y., Aburatani H., Niki T., Sohara Y., Sugiyama Y., Mano H. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi K., Soda M., Togashi Y., Suzuki R., Sakata S., Hatano S., Asaka R., Hamanaka W., Ninomiya H., Uehara H., Lim Choi Y., Satoh Y., Okumura S., Nakagawa K., Mano H., Ishikawa Y. Nat. Med. 2012;18:378–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

