Identification of imidazo[1,2- b]pyridazine TYK2 pseudokinase ligands as potent and selective allosteric inhibitors of TYK2 signalling
- PMID: 30108788
- PMCID: PMC6071835
- DOI: 10.1039/c6md00560h
Identification of imidazo[1,2- b]pyridazine TYK2 pseudokinase ligands as potent and selective allosteric inhibitors of TYK2 signalling
Abstract
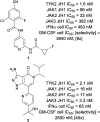
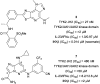
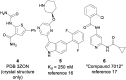
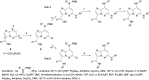
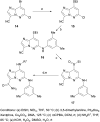
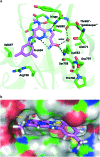
As a member of the Janus (JAK) family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases, TYK2 mediates the signaling of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-12, IL-23 and type 1 interferon (IFN), and therefore represents an attractive potential target for treating the various immuno-inflammatory diseases in which these cytokines have been shown to play a role. Following up on our previous report that ligands to the pseudokinase domain (JH2) of TYK2 suppress cytokine-mediated receptor activation of the catalytic (JH1) domain, the imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine (IZP) 7 was identified as a promising hit compound. Through iterative modification of each of the substituents of the IZP scaffold, the cellular potency was improved while maintaining selectivity over the JH1 domain. These studies led to the discovery of the JH2-selective TYK2 inhibitor 29, which provided encouraging systemic exposures after oral dosing in mice. Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) was identified as an off-target and potential liability of the IZP ligands, and selectivity for TYK2 JH2 over this enzyme was obtained by elaborating along selectivity vectors determined from analyses of X-ray co-crystal structures of representative ligands of the IZP class bound to both proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Small Molecule Tyrosine Kinase 2 Pseudokinase Ligands Block Cytokine-Induced TYK2-Mediated Signaling Pathways.Front Immunol. 2022 May 20;13:884399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.884399. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35693820 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of N-Methyl Nicotinamide and N-Methyl Pyridazine-3-Carboxamide Pseudokinase Domain Ligands as Highly Selective Allosteric Inhibitors of Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2).J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 24;62(20):8953-8972. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00443. Epub 2019 Jul 17. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31314518
-
Deucravacitinib is an allosteric TYK2 protein kinase inhibitor FDA-approved for the treatment of psoriasis.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Mar;189:106642. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106642. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36754102 Review.
-
Structural and Functional Characterization of the JH2 Pseudokinase Domain of JAK Family Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2).J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 6;290(45):27261-27270. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.672048. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26359499 Free PMC article.
-
Tyk2 Targeting in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 8;24(4):3391. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043391. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperactivation of Oncogenic JAK3 Mutants Depend on ATP Binding to the Pseudokinase Domain.Front Oncol. 2018 Dec 3;8:560. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00560. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30560087 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of JAK1 Pseudokinase Domain in Cytokine Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 27;12(1):78. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010078. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31892268 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and molecular modeling of phenylenediamine-phenylhydrazine-formaldehyde terpolymer (PPHF) as potent anti-inflammatory agent.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 6;9(7):e18067. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18067. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37483726 Free PMC article.
-
New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 19;15(3):374. doi: 10.3390/ph15030374. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translating current basic research into future therapies for neurofibromatosis type 1.Br J Cancer. 2020 Jul;123(2):178-186. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0903-x. Epub 2020 May 22. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32439933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clark J. D., Flanagan M. E., Telliez J.-B. J. Med. Chem. 2014;57:5023–5038. - PubMed
-
- For a review of progress towards JAK1-selective inhibitors see: Menet C. J., Mammoliti O., López-Ramos M., Future Med. Chem., 2015, 7 , 203 –235 . - PubMed
-
- Inhibition of JAK2 could result in anemia and other undesired hematopoiteic defects: Vincenti F., Tedesco Silva H., Busque S., O'Connell P., Friedewald J., Cibrik D., Budde K., Yoshida A., Cohney S., Weimar W., Kim Y. S., Lawendy N., Lan S.-P., Kudlacz E., Krishnaswami S., Chan G., Am. J. Transplant., 2012, 12 , 2446 –2456 . - PubMed
-
- For a review of the use of Ustekinumab in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis see: Croxtall J. D., Drugs, 2011, 71 , 1733 –1753 . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

