Design, synthesis, crystal structure and fungicidal activity of (E)-5-(methoxyimino)-3,5-dihydrobenzo[ e][1,2]oxazepin-4(1 H)-one analogues
- PMID: 30108816
- PMCID: PMC6072479
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00025a
Design, synthesis, crystal structure and fungicidal activity of (E)-5-(methoxyimino)-3,5-dihydrobenzo[ e][1,2]oxazepin-4(1 H)-one analogues
Erratum in
-
Correction: Design, synthesis, crystal structure and fungicidal activity of (E)-5-(methoxyimino)-3,5-dihydrobenzo[e][1,2]oxazepin-4(1H)-one analogues.Medchemcomm. 2017 Jun 12;8(6):1366. doi: 10.1039/c7md90022h. eCollection 2017 Jun 1. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 30109867 Free PMC article.
Abstract
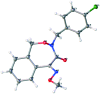
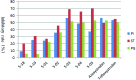
A practical method of four-step synthesis towards novel (E)-5-(methoxyimino)-3,5-dihydrobenzo[e][1,2]oxazepin-4(1H)-one antifungals is presented, where a commercially available pesticide and pharmacology intermediate, (E)-methyl 2-(2-(bromomethyl)phenyl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetate (1), was used as starting material. These compounds were confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, high-resolution mass spectroscopy and X-ray crystal structure. Via in vitro fungicidal evaluation, the moderate to high activities of several compounds against eight phytopathogenic fungi were demonstrated. Especially, the fungicidal activities of compounds 5-03 and 5-09 were comparable to those of the controls azoxystrobin and trifloxystrobin in precise virulence measurements for four fungi. These results suggested that dihydrobenzo[e][1,2]oxazepin-4(1H)-one analogues could be considered as potential fungicidal candidates for crop protection.
Figures



References
-
- Noskov V. G., Kalinina L. N., Noskova M. N., Kruglyak Y. L., Strukov O. G., Bezrukovet A. P. Pharm. Chem. J. 1997;31:431–434.
- Simon L., Fülöp F., Bernáth G., Argay G., Kálmán A., Sohár P. Acta Pharm. Hung. 1996;66:111–118. - PubMed
- Frost J., Lardenois P., Bertin J., Saarmets A. and Rousselle C., EP, EP0351282, 1993.
- Evans P., Thomas E. J. and Davies R. H., EP, EP1294697, 2003.
- Takahashi M., Onizawa S., Satoh T. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1974;47:2724–2726.
- Ozeki M., Muroyama A., Kajimoto T., Watanabe T., Wakabayashi K., Node M. Synlett. 2009;11:1781–1784.
- Taher A. T., Mohammed L. W. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013;36:684–693. - PubMed
- Davion Y., Guillaumet G., Leger J. M., Jarry C., Lesur B., Merour J. Y. Heterocycles. 2004;63:1093–1112.
-
- Harris P. A., King B. W., Bandyopadhyay D., Berger S. B., Campobasso N., Capriotti C. A. J. Med. Chem. 2016;59:2163–2178. - PubMed
-
- Gao Z., Ma Y., Zhao D., Zhang X., Zhou H., Liu H. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014;92:358–368. - PubMed
-
- Ndubaku C. O., Heffron T. P., Staben S. T., Baumgardner M., Blaquiere N., Bradley E. J. Med. Chem. 2013;56:4597–4610. - PubMed
-
- Liu X. H., Jia Y. M., Song B. A., Pang Z. X., Yang S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013;23:720–723. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

