Synthesis and biological evaluation of chalcone-linked pyrazolo[1,5- a]pyrimidines as potential anticancer agents
- PMID: 30108891
- PMCID: PMC6084153
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00193b
Synthesis and biological evaluation of chalcone-linked pyrazolo[1,5- a]pyrimidines as potential anticancer agents
Abstract
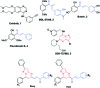
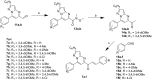
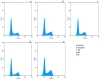
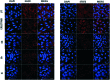
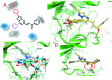
A series of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines substituted at C5 with 1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one (6a-q) and 3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one (7a-k) was synthesized and evaluated for antiproliferative activity. Among them, 6h was found to be the most active compound against the MDA-MB-231 cell line with an IC50 of 2.6 μM . The antiproliferative activity of this series of compounds ranged from 2.6 to 34.9 μM against A549 (lung cancer), MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer) and DU-145 (prostate cancer) cell lines. FACS analysis revealed that these hybrids arrest the cell cycle at the subG1 phase. Western blot analysis and an immunofluorescence assay showed the inhibition of the EGFR and STAT3 axis, which plays an important role in cell survival and apoptosis. Western blot and RT-PCR analyses that displayed an increase in apoptotic proteins such as p53, p21 and Bax and a decrease in the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and procaspase-9 confirmed the ability of these hybrids to trigger cell death by apoptosis. Molecular docking studies described the binding of these hybrids to the ATP binding site of EGFR.
Figures



References
-
- Torre L. A., Bray F., Siegel R. L., Ferlay J., Lortet-Tieulent J., Jemal A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Bray F., Jemal A., Grey N., Ferlay J., Forman D. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:790–801. - PubMed
-
- Zugazagoitia J., Guedes C., Ponce S., Ferrer I., Molina-Pinelo S., Paz-Ares L. Clin. Ther. 2016;38:1551–1566. - PubMed
-
- Backes A., Zech B., Felber B., Klebl B., Müller G. Expert Opin. Drug Discovery. 2008;3:1427–1449. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

