Synthesis and biological evaluation of rapamycin-derived, next generation small molecules
- PMID: 30108899
- PMCID: PMC6072512
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00474e
Synthesis and biological evaluation of rapamycin-derived, next generation small molecules
Abstract
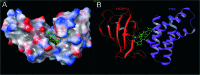
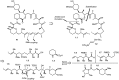
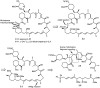
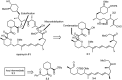
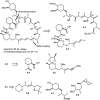
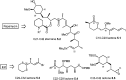
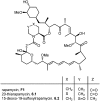
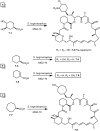
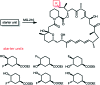
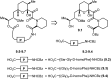
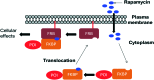
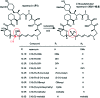
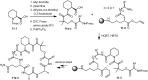
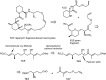
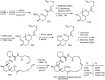
Over the years, rapamycin has attracted serious attention due to its remarkable biological properties and as a potent inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein through its binding with FKBP-12. Several efficient strategies that utilize synthetic and biosynthetic approaches have been utilized to develop small molecule rapamycin analogs or for synthesizing hybrid compounds containing a partial rapamycin structure to improve pharmacokinetic properties. Herein, we report selected case studies related to the synthesis of rapamycin-derived compounds and hybrid molecules to explore their biological properties.
Figures
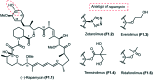
References
-
- Sehgal S. N., Baker H., Vezina C. J. Antibiot. 1975;28:727–732. - PubMed
-
- Vezina C., Kudelski A., Sehgal S. N. J. Antibiot. 1975;28:721–726. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin D., Colombi M., Moroni C., Hall M. N. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2011;10:868–880. - PubMed
-
- Schmelzle T., Hall M. N. Cell. 2000;103:253–262. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

