Highly efficient antibody purification with controlled orientation of protein A on magnetic nanoparticles
- PMID: 30108904
- PMCID: PMC6072530
- DOI: 10.1039/c7md00468k
Highly efficient antibody purification with controlled orientation of protein A on magnetic nanoparticles
Abstract
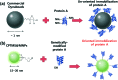
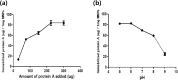
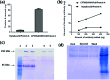
In this study, we prepared protein A grafted magnetic nanoparticles for the industrial large-scale purification of antibodies with enhancement of binding capacity and immobilization by controlled orientation with chlorophenylsilane (CPTMS) on the surface. For site-specific immobilization of protein A, genetically modified protein A with a cysteine residue was expressed in E. coli and purified by affinity chromatography. To improve the surface area to volume ratio and increase the immobilization amount of protein A, chlorophenylsilane functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (CPTMS@MNPs) were prepared, which are smaller nanoparticles with an average diameter of 20 nm compared to commercial magnetic microparticles (Dynabeads) with an average size of 2.8 μm. The CPTMS@MNPs showed the enhancement of protein A immobilization and binding capacity to antibodies, being 11.5-fold and 7-fold higher than those of commercial Dynabeads, respectively. In addition, the CPTMS@MNPs retained about 80% of the initial protein binding capacity until the third stage of recycling. Therefore, protein A grafted CPTMS@MNPs may be useful for the industrial large-scale purification of antibodies.
Figures
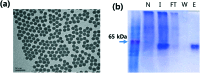
Similar articles
-
State of the art on the separation and purification of proteins by magnetic nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Oct 4;21(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02123-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37794459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
Regulation of the catalytic behavior of pullulanases chelated onto nickel (II)-modified magnetic nanoparticles.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2017 Jun;101:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2017. PMID: 28433193
-
Direct purification and immobilization of his-tagged enzymes using unmodified nickel ferrite NiFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 6;13(1):21549. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48795-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38057439 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers for enzymes immobilization: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Dec;120(Pt B):2530-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.025. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 30201561 Review.
Cited by
-
State of the art on the separation and purification of proteins by magnetic nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Oct 4;21(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02123-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37794459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct Affinity Ligand Immobilization onto Bare Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enables Efficient Magnetic Separation of Antibodies.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Jun 17;7(6):3942-3952. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00280. Epub 2024 May 13. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38740514 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of a Heptapeptide-Modified Poly(glycidyl Methac-Rylate) Nanosphere for Oriented Antibody Immobilization and Immunoassay.Molecules. 2024 Sep 29;29(19):4635. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194635. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407565 Free PMC article.
-
Immobilizing calcium-dependent affinity ligand onto iron oxide nanoparticles for mild magnetic mAb separation.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2024 Nov 26;45:e00864. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00864. eCollection 2025 Mar. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39691100 Free PMC article.
-
Transient proteolysis reduction of Nicotiana benthamiana-produced CAP256 broadly neutralizing antibodies using CRISPR/Cas9.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 18;13:953654. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.953654. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36061808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottshalk U., Brorson K., Shukla A. Nat. Methods. 2012;30:489. - PubMed
-
- Jungbauer A., Hahn R. Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev. 2004;7:248. - PubMed
-
- Ishihara T., Nakajima N., Kadoya T. J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010;878:2141. - PubMed
-
- Hahn R., Schlegel R., Jungbauer A. J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003;790:35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

