Effect of isouronium/guanidinium substitution on the efficacy of a series of novel anti-cancer agents
- PMID: 30108964
- PMCID: PMC6072505
- DOI: 10.1039/c8md00089a
Effect of isouronium/guanidinium substitution on the efficacy of a series of novel anti-cancer agents
Abstract
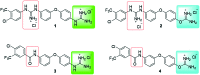
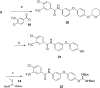
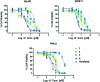
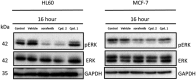
Considering our hypothesis that the guanidinium moiety in the protein kinase type III inhibitor 1 interacts with a phosphate of ATP within the hinge region, the nature of the interactions established between a model isouronium and the phosphate groups of ATP was computationally analysed indicating that an isouronium derivative of 1 will interact in a similar manner with ATP. Thus, a number of compounds were prepared to assess the effect of the guanidinium/isouronium substitution on cancer cell growth; additionally, the molecular shortening and conformational change induced by replacing the di-substituted guanidine-linker of 1 by an amide was explored. The effect of these compounds on cell viability was tested in human leukaemia, breast cancer and cervical cancer cell lines and the resulting IC50 values were compared with those of the lead compound 1. Replacement of the di-substituted guanidine-linker by an amide results in the loss of cytotoxicity; however, substitution of the mono-substituted guanidinium by an isouronium cation seems to be beneficial for cell growth inhibition. Additionally, the effect of these compounds on the MAPK/ERK pathway was studied by means of Western blotting and the results indicate that the isouronium derivative 2 decreases the levels of phosphorylated, and thus activated, ERK (pERK) both in leukaemia and breast cancer cells, whereas lead compound 1 only shows an effect on pERK levels in breast cancer cells. This confirms that both compounds could interfere with the MAPK/ERK pathway although other targets cannot be ruled out.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Novel 3,4'-Substituted Diaryl Guanidinium Derivatives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Dec 21;13(12):485. doi: 10.3390/ph13120485. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33371382 Free PMC article.
-
Isouronium and N-hydroxyguanidinium derivatives as Cell growth inhibitors: A comparative study.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Jul 19;117:269-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.047. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27108161
-
Guanidinium-based derivatives: searching for new kinase inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Jun 23;81:427-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.05.025. Epub 2014 May 9. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24858546
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
Guanidinium group: a versatile moiety inducing transport and multicompartmentalization in complementary membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Apr;1778(4):811-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.12.003. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18178146 Review.
Cited by
-
Allantodapsone is a Pan-Inhibitor of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion to Fibrinogen, Loricrin, and Cytokeratin 10.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0117521. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01175-21. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35647689 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Novel 3,4'-Substituted Diaryl Guanidinium Derivatives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Dec 21;13(12):485. doi: 10.3390/ph13120485. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33371382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen P. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2002;1:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Wu P., Nielsen T. E., Clausen M. H. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015;36:422–439. - PubMed
-
- Fabian M. A., Biggs W. H., Treiber D. K., Atteridge C. E., Azimioara M. D., Benedetti M. G., Carter T. A., Ciceri P., Edeen P. T., Floyd M., Ford J. M., Galvin M., Gerlach J. L., Grotzfeld R. M., Herrgard S., Insko D. E., Insko M. A., Lai A. G., Lelias J. M., Mehta S. A., Milanov Z. V., Velasco A. M., Wodicka L. M., Patel H. K., Zarrinkar P. P., Lockhart D. J. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:329–336. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Yang P. L., Gray N. S. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2009;9:28–39. - PubMed
-
- Fang Z., Grutter C., Rauh D. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013;8:58–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

