Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of benzimidazole-rhodanine conjugates as potent topoisomerase II inhibitors
- PMID: 30109008
- PMCID: PMC6072309
- DOI: 10.1039/c8md00278a
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of benzimidazole-rhodanine conjugates as potent topoisomerase II inhibitors
Abstract
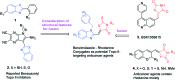
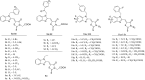
In this study, a series of benzimidazole-rhodanine conjugates were designed, synthesized and investigated for their topoisomerase II (Topo II) inhibitory and cytotoxic activities. The results from Topo II-mediated pBR322 DNA relaxation and cleavage assays showed that the synthesized compounds might act as Topo II catalytic inhibitors. Certain compounds displayed potent Topo II inhibition at 10 μM. The cytotoxic activities of these compounds against HeLa, A549, Raji, PC-3, MDA-MB-201, and HL-60 cancer cell lines were evaluated. The results indicated that these compounds exhibited strong antiproliferative activity. A good relationship was observed between the Topo II inhibitory potency and the cytotoxicity of these compounds. The structure-activity relationship revealed that the electronic effects, the phenyl group, and the rhodanine moiety were particularly important for the Topo II inhibitory potency and cytotoxicity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel carbazole-rhodanine conjugates as topoisomerase II inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 May 1;28(8):1320-1323. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.03.017. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 29545100
-
Design, synthesis, topoisomerase I & II inhibitory activity, antiproliferative activity, and structure-activity relationship study of pyrazoline derivatives: An ATP-competitive human topoisomerase IIα catalytic inhibitor.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Apr 15;24(8):1898-908. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.03.017. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26988802
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 7-alkylamino substituted benzo[a]phenazin derivatives as dual topoisomerase I/II inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Mar 6;92:540-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.024. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25599951
-
Dihydroxylated 2,6-diphenyl-4-chlorophenylpyridines: Topoisomerase I and IIα dual inhibitors with DNA non-intercalative catalytic activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Jun 16;133:69-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.03.048. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28384547
-
Recent advances in the development of dual topoisomerase I and II inhibitors as anticancer drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(35):4270-90. doi: 10.2174/092986710793361252. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20939813 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of DNA Intercalators Based on 4-Carboranyl-1,8-Naphthalimides: Investigation of Their DNA-Binding Ability and Anticancer Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4598. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094598. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562989 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological studies of carbazole-thiosemicarbazone hybrids as potential topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2025 May 9. doi: 10.1039/d5md00234f. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40438287 Free PMC article.
-
Benzimidazole chemistry in oncology: recent developments in synthesis, activity, and SAR analysis.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 3;15(23):18593-18647. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01077b. eCollection 2025 May 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40463335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Natural and Synthetic Chalcones as Anticancer Agents Targeting Topoisomerase Enzymes.Molecules. 2025 Jun 6;30(12):2498. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122498. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, Synthesis and Anti-Tumor Activity of Novel Benzimidazole-Chalcone Hybrids as Non-Intercalative Topoisomerase II Catalytic Inhibitors.Molecules. 2020 Jul 12;25(14):3180. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143180. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32664629 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

