Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma, Biphasic Type: An Unusual and Insidious Case of Rapidly Progressive Small Blue Cell Tumor
- PMID: 30109162
- PMCID: PMC6082884
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2749
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma, Biphasic Type: An Unusual and Insidious Case of Rapidly Progressive Small Blue Cell Tumor
Abstract
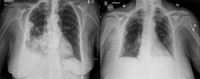
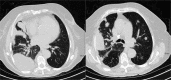
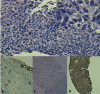
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a rare neoplasm. It predominantly affects elderly individuals aged over 70 years presenting with a unilateral pleural tumor usually associated with previous asbestos exposure. The respiratory symptoms are associated with ipsilateral pleural involvement with concomitant pleural effusions. The diagnosis of MPM is established by the morphologic and immunohistochemical features of a cytologic specimen. MPM can present as three histologic subtypes: epithelioid, sarcomatoid, or biphasic. We present a case of an 85-year-old Caucasian female with a history of occupational asbestos exposure. She complained of 1-week history of progressive sharp right flank and scapular pain with mild shortness of breath, dry cough and pleuritic chest pain. CT of the chest showed a large loculated right pleural effusion with adjacent pleural thickening. CT abdomen and pelvis was negative for other neoplastic findings. CT-guided core biopsy of the right pleural-based mass was positive for a spindle to plasmacytoid small blue cell tumor. An extensive immunohistochemical panel was non-specific. A focal OSCAR keratin and WT-1 expression in the absence of carcinoma markers, a malignant mesothelioma, biphasic type was diagnosed. Further workup with PET-CT and cytotoxic chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitors was recommended by oncology. The patient refused further imaging and treatment, and palliative care was consulted.
Keywords: asbestos; malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Rare Case of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma in a Young Healthy Male Without Asbestos Exposure.Cureus. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):e17199. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17199. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34540427 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant pleural neoplasm with both differentiation of epithelioid mesothelioma and squamous-cell carcinoma, a rare phenomena.Diagn Cytopathol. 2021 Jun;49(6):E234-E237. doi: 10.1002/dc.24686. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Diagn Cytopathol. 2021. PMID: 33347735
-
Unusual features of malignant pleural mesothelioma metastatic to the mediastinal lymph nodes.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2008 May;16(3):301-7. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181507893. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2008. PMID: 18301236
-
On the diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A necropsy-based study of 171 cases (1997-2016).Tumori. 2019 Aug;105(4):304-311. doi: 10.1177/0300891618765538. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Tumori. 2019. PMID: 29714657 Review.
-
[Malignant pleural mesothelioma: diagnosis and treatment].Rev Pneumol Clin. 2013 Feb;69(1):26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.pneumo.2012.12.003. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Rev Pneumol Clin. 2013. PMID: 23333048 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A Gelatinous Pleural Effusion as a Diagnostic Clue.Cureus. 2023 Mar 9;15(3):e35942. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35942. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37038561 Free PMC article.
-
Near Missed Case of Occupational Pleural Malignant Mesothelioma, a Case Report and Latest Therapeutic Options.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 10;19(22):14763. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214763. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malignant mesothelioma. [Oct;2018 ];Robinson BW, Musk AW, Lake RA. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(05)67025.... Lancet. 2005 366:397–408. - PubMed
-
- The global burden of disease due to occupational carcinogens. [Jun;2018 ];Driscoll T, Nelson DI, Steenland K, et al. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ajim.20210. Am J Ind Med. 2005 48:419–431. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
