Personalized medicine in non-small cell lung cancer: a review from a pharmacogenomics perspective
- PMID: 30109178
- PMCID: PMC6089847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.04.005
Personalized medicine in non-small cell lung cancer: a review from a pharmacogenomics perspective
Abstract
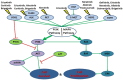
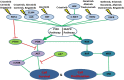
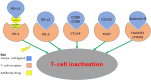
Non-small cell lung cancer is a prevalent and rapidly-expanding challenge to modern medicine. While generalized medicine with traditional chemotherapy yielded comparatively poor response rates and treatment results, the cornerstone of personalized medicine using genetic profiling to direct treatment has exalted the successes seen in the field and raised the standard for patient treatment in lung and other cancers. Here, we discuss the current state and advances in the field of personalized medicine for lung cancer, reviewing several of the mutation-targeting strategies that are approved for clinical use and how they are guided by patient genetic information. These classes include inhibitors of tyrosine kinase (TKI), anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), and monoclonal antibodies. Selecting from these treatment plans and determining the optimal dosage requires in-depth genetic guidance with consideration towards not only the underlying target genes but also other factors such as individual metabolic capability and presence of resistance-conferring mutations both directly on the target gene and along its cascade(s). Finally, we provide our viewpoints on the future of personalized medicine in lung cancer, including target-based drug combination, mutation-guided drug design and the necessity for data of population genetics, to provide rough guidance on treating patients who are unable to get genetic testing.
Keywords: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; Inhibitor; Monoclonal antibody; Non-small cell lung cancer; Personalized medicine; Pharmacogenomics; Tyrosine kinase.
Figures
References
-
- Torre L.A., Siegel R.L., Ward E.M., Jemal A. Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends—an update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016;25:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Xu J., Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Schiller J.H., Harrington D., Belani C.P., Langer C., Sandler A., Krook J. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L., Alexander R.E., MacLennan G.T., Cummings O.W., Montironi R., Lopez-Beltran A. Molecular pathology of lung cancer: key to personalized medicine. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:347–369. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

