Targeting ERK, an Achilles' Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy
- PMID: 30109180
- PMCID: PMC6089851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.01.008
Targeting ERK, an Achilles' Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy
Abstract
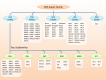
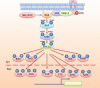
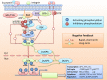
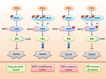
The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway, often known as the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signal cascade, functions to transmit upstream signals to its downstream effectors to regulate physiological process such as cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and death. As the most frequently mutated signaling pathway in human cancer, targeting the MAPK pathway has long been considered a promising strategy for cancer therapy. Substantial efforts in the past decades have led to the clinical success of BRAF and MEK inhibitors. However, the clinical benefits of these inhibitors are compromised by the frequently occurring acquired resistance due to cancer heterogeneity and genomic instability. This review briefly introduces the key protein kinases involved in this pathway as well as their activation mechanisms. We also generalize the correlations between mutations of MAPK members and human cancers, followed by a summarization of progress made on the development of small molecule MAPK kinases inhibitors. In particular, this review highlights the potential advantages of ERK inhibitors in overcoming resistance to upstream targets and proposes that targeting ERK kinase may hold a promising prospect for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Drug resistance; ERK inhibitor; ERK kinase; Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Mitogen-activated protein kinases.
Figures

References
-
- Dhillon A.S., Hagan S., Rath O., Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–3290. - PubMed
-
- Vetter I.R., Wittinghofer A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science. 2001;294:1299–1304. - PubMed
-
- Mitin N., Rossman K.L., Der C.J. Signaling interplay in Ras superfamily function. Curr Biol. 2005;15:R563–R574. - PubMed
-
- Schubbert S., Shannon K., Bollag G. Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:295–308. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

